Expert Systems In AI: Informative Guide Of Everything You Need To Know
Table of Contents

- jaro education
- 14, May 2024
- 3:03 pm
Overview
In today’s rapidly evolving world, expert systems in AI (Artificial Intelligence) play a crucial role in solving complex decision-making issues as human experts in a specific domain. The expert system operates by retrieving and applying specialized knowledge from its knowledge base to address user queries and provide solutions. Built on artificial intelligence (AI), expert systems simulate the decision-making capabilities of a human expert in various domains. These systems are extensively employed across sectors like healthcare, manufacturing, finance, and customer service, aiding in complex decision-making processes that would otherwise require expert intervention. Their use ranges from diagnosing diseases to optimizing supply chains, financial risk assessments, and enhancing customer experiences with personalized recommendations.
In this guide, we will delve into the architecture of expert systems, discussing how they function, the intricacies of their knowledge representation, and the reasoning mechanisms they employ. We’ll explore the core characteristics and components of expert systems, including the knowledge base, inference engine, and user interface. Additionally, we will highlight the advantages and limitations that come with implementing expert systems and provide real-world applications to showcase their significance across industries. So, let’s dive into the multifaceted world of expert systems in AI!
What is an Expert System?
- Introduced in the 1970s by the researchers of Stanford University, Computer Science Department, an expert system is an AI software that is designed to assist humans in resolving the most complex problems of any particular domain.
- The system works based on the knowledge received from an expert stored in its knowledge base, thus considering the highest level of human intelligence and expertise.
- The more knowledge stored in its knowledge base, the greater would be its performance.
- AI and expert systems are proficient in expressing and interpreting knowledge in a particular area.
- One of the most common examples is getting misspelling suggestions if there is a typo error in the Google search box.
Popular Examples of Expert Systems in AI
Below mentioned are some popular types of expert systems:
| Example | Description |
|---|---|
| DENDRAL | Created as a chemical analysis expert system, DENDRAL was an AI project that was used to spot unidentified organic molecules with the support of its mass spectra and knowledge base of organic chemistry. |
| MYCIN | An early backward chaining expert system, it was designed to discover the bacteria causing serious infections like bacteraemia and meningitis. It was also used to recommend antibiotics and identify blood clotting diseases. |
| PXDES | PXDES (Protein X-Ray Diffraction Expert System) is a type of expert system that is used to identify the level of lung cancer. For this, a picture is taken from the upper body, which appears like a shadow, and this shadow helps detect the level of disease. |
| CaDet | CaDet (Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment) is another type of expert system which helps identify cancer at its initial stages by using a knowledge base of medical data and recommend treatment options. |
Characteristics of Expert Systems
*javatpoint.com
One of the main characteristics of expert systems is their capability of decision-making based on knowledge. Expert systems in AI characteristically rely on a set of reasoning rules. Their ability to learn and update their knowledge base with the latest information allows them to enhance their accuracy eventually. So, here is a list of some of the major characteristics of expert systems in AI.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| High Performance | Expert system architecture is designed to provide a high level of performance with efficiency and accuracy. They can solve any type of complex issue of a particular domain by using the reasoning and implication rules, making them more reliable for providing precise results. |
| Reliable | Expert system diagrams are designed to provide reliable and accurate results. Their knowledge base is carefully organised and updated with the latest data, ensuring that AI and expert systems recommend more reliable and trustworthy output. |
| Understandable | The expert system diagram is structured in a way that can be easily understandable for end-users. Its knowledge base and rules are in human languages, hence providing results in the same way. |
| Highly Responsive | Structure of Expert systems in AI provide a quick response by processing data and applying rules, making them highly responsive for time-sensitive conditions. |
| Adaptability | Expert systems can adapt to new information and scenarios. By learning from past experiences or new data, they can adjust their decision-making process to accommodate novel situations, making them more flexible over time. |
| Knowledge Representation | Expert systems use symbolic knowledge representation, which allows complex real-world information to be encoded and processed in an organized manner. This structure supports the system's reasoning abilities and helps achieve more accurate outcomes. |
| Consistency | Unlike human decision-makers who may be influenced by emotions or fatigue, expert systems maintain consistent decision-making. The rules and knowledge base remain the same for similar situations, ensuring dependable results. |
| Scalability | The structure of expert systems allows for scalability. As the complexity of the problems grows, the system can be expanded with additional rules or knowledge without a significant drop in performance. |
| Error Reduction | Due to their reliance on well-defined rules and data, expert systems help minimize errors that can result from human oversight or knowledge gaps, improving the overall quality of decisions. |
Components of Expert Systems in AI
The following are the components of expert systems in AI:
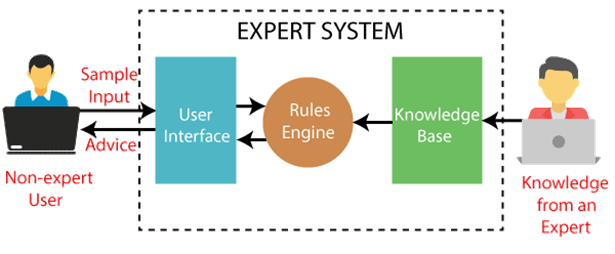
- User Interface: One of the key components of an expert system, the user interface helps users interact with the expert system and input data in an understandable format. After the process of data, the expert system shows the output to the users, making it more user-friendly for solving input-related issues. In simple words, a user interface allows a user to communicate with an expert system for a problem-solving solution.
- Knowledge Base: In an expert system, the knowledge base is the storehouse of information for specific domains. It comprises facts, heuristics, data and rules in a structured way. The knowledge base is maintained and updated on a regular basis with recent and accurate information.
- Inference Engine: Known as the brain of the expert system, the inference engine collects information stored in the knowledge base and applies inference rules to derive an error-free conclusion as per the user’s queries. It uses the following modes to derive the solution from the knowledge base and input data.
- Forward Chaining: Also known as the forward reasoning method, forward chaining starts from an initial state in the knowledge base and applies rules in the forward direction to draw conclusions to the known facts. It repeats this process until the goal is met.
- Backward Chaining: Backward chaining, also known as the backward reasoning method in an inference engine, starts from the goal and works in a backward direction to determine the known facts.
- Explanation Systems: Explanation systems are used to explain the produced conclusion, improving transparency and making it user-friendly for users. It also helps users understand the reasoning process of the expert system.
Participants Involved in the Development of Expert Systems in AI
*javatpoint.com
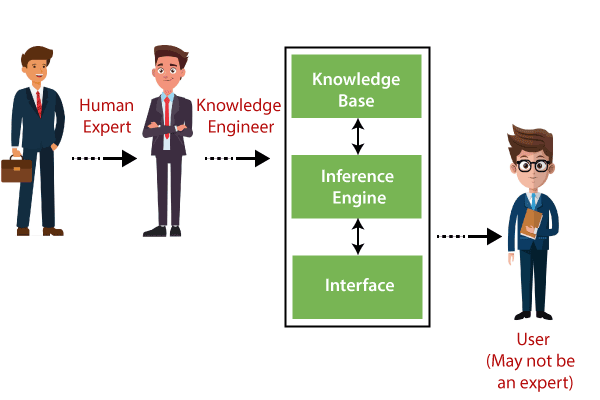
Several participants are involved in the development of expert systems in AI. Some of the primary participants are:
- Expert: The experts are those professionals who are specialised in a particular field. They provide the input data, rules and facts that create the knowledge base. Their knowledge and expertise are crucial for developing an accurate and trustworthy expert system.
- Knowledge Engineer: The knowledge engineer is the person who is responsible for organising, maintaining and encoding the knowledge into the system’s knowledge base provided by the domain expert, in a structured format.
- End-user: The end-user is a person or group who interacts with the expert system to find solutions or recommendations for complex problems.
Why Use Expert Systems in AI?
It is mandatory for users to understand why to use expert systems in AI. So, below are several benefits mentioned that make expert systems more usable and valuable for different domains or industries, which include:
| Benefits | Description |
|---|---|
| Accuracy | Created on the knowledge base that is maintained and updated frequently, expert systems in AI make sure that the explanations or results provided by them are accurate and reliable. |
| Efficiency | Structure of Expert systems can reduce the time and effort that is required to peruse and understand data while automating the decision-making processes, thus increasing efficiency and productivity. |
| Capabilities | AI and expert systems have abilities to process a large amount of data accurately and within a short period. They can solve complex issues and provide solutions based on knowledge and reasoning rules. |
| Adaptability | Different areas or industries can easily adopt expert systems as their knowledge base is maintained and updated with the new information, making them more adaptable. |
| Consistency | Expert systems offer consistent performance without being influenced by emotional or personal biases. They provide uniform decisions based on the same knowledge base and reasoning, ensuring reliability over time. |
| Availability | Expert systems can be operational 24/7, providing access to expertise at any time without the constraints of human availability. This is especially valuable in industries that require constant monitoring and decision-making, such as healthcare or finance. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | While initial setup can be resource-intensive, expert systems reduce the need for human expertise in repetitive tasks, lowering operational costs in the long run. They can minimize errors and reduce the need for multiple consultations with human experts. |
| Real-Time Solutions | Expert systems can provide instant responses and solutions in real-time, which is crucial in fast-paced industries such as logistics, finance, or emergency management, where immediate decisions are essential. |
Advantages of Expert Systems in AI
The following are the advantages of expert systems in AI:
| Advantages | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Decision-making | Expert systems provide accurate solutions or recommendations based on the knowledge and rules of the specific domain stored in their knowledge base. This process enhances decision-making and eliminates human errors. |
| Cost-effective | Expert systems are relatively cost-effective solutions compared to employing multiple domain human experts. The expert system can be easily adapted and used by several users, making it an affordable solution for different domains. |
| Increased Efficiency | Expert systems in AI lessen the time and effort by automating decision-making processes, thus increasing efficiency and productivity in different organisations. |
| Enhanced Accessibility | Expert systems are accessible to users for domain-specific knowledge and expertise. They can use expert systems to increase insights and informed decision-making in fields where they lack proficiency. |
Limitations of Expert Systems
| Limitation | Description |
|---|---|
| Limited Domain | Expert systems architecture is designed to solve problems for specific domains and may not be used for domains outside their scope. They depend on the accuracy of their knowledge base. So, if the knowledge base is not complete with all the required information, then the expert system may not work perfectly. |
| Maintenance and Updates | Steady maintenance and updates are required for expert systems in AI to make the knowledge base accurate and updated. This is where continuous efforts are required from an engineer or expert to make sure that the efficiency of the expert system is maintained. |
| Lack of Common Sense | There may be a lack of common sense in expert systems, reasoning and solving uncertain situations efficiently. They solely rely on the data and rules stored in the knowledge base and may lack adaptability to situations that need human imagination. |
| Lack of Learning and Adaptability | Expert systems architectures are not capable of acquiring new information or adapt to changing situations. They solely depend on their knowledge base and rules stored during their development, which may lead to a lack of limited learning and adaptability. |
| Overdependence on Expert Knowledge | In fact, expert systems are overdependent on the knowledge provided by the expert. If the knowledge of the expert is unfair or incomplete, then it may affect the accuracy and dependability of the expert system's decision-making solutions. |
| Inability to Handle Ambiguity | Expert systems may struggle when dealing with ambiguous or incomplete data. Unlike humans, who can make decisions based on intuition or partial information, expert systems require structured data and predefined rules, making them less effective in situations with uncertainty. |
| High Development Costs | Creating an expert system is often costly and time-consuming. It requires extensive collaboration between domain experts, software engineers, and knowledge engineers. The process of collecting, structuring, and maintaining a comprehensive knowledge base can result in high initial and ongoing costs. |
| Difficulties in Knowledge Representation | Translating the expert’s knowledge into a format that can be processed by the system is not always straightforward. Some forms of knowledge, such as tacit knowledge or intuition-based insights, are difficult to capture and encode in an expert system. |
| Lack of Flexibility | Expert systems lack flexibility when it comes to adapting to new domains or tasks outside their predefined scope. Unlike human experts who can apply their knowledge across various fields, expert systems are typically constrained to a narrow set of rules and cannot easily be transferred to other areas. |
In spite of these limitations, expert systems in AI are considered to be valuable options in helping provide decision-making solutions in specific domains.
Applications of Expert Systems in Artificial Intelligence
There are different applications of expert systems in Artificial Intelligence in several domains, which include:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Finance Domain | Expert systems in AI are used in the finance domain for solving problems, such as risk assessment, investment portfolio management and scam detection. They can evaluate financial data and provide solutions for making informed decisions for investment or noticing possible scams. |
| Knowledge Domain | AI and Expert systems are used in knowledge domains, such as legal, strategic, academic property and patent searches, where they can quickly review and infer large volumes of data to provide decision-making solutions. |
| Designing and Manufacturing | Used in the domain of design and manufacturing for functions, such as process optimisation, product design, quality control and fault detection, expert systems can evaluate complex data queries and provide solutions to enhance the design or manufacturing processes. |
| Planning and Scheduling | Expert systems in AI are applied in planning and scheduling domains for analysing data and providing decision-making solutions for tasks, such as transportation, project management and logistics. |
| Diagnosis and Troubleshooting of Devices | Expert systems are designed to be used in the diagnosis and troubleshooting of devices, such as computer systems, automobiles and medical equipment. They can scan symptoms and provide accurate recommendations or solutions for detecting and determining issues. |
Conclusion
We hope you understand how expert systems in AI are valuable and powerful programs that use knowledge and rules specific to domains to provide accurate and trustworthy solutions or recommendations. They have been used in several domains successfully, such as finance domain, planning and scheduling domain, knowledge domain, diagnosis and troubleshooting domain and designing and manufacturing domain.
In conclusion, AI and expert systems are reliable and helpful for determining complex issues quickly as per users’ queries. Additionally, from high performance, adaptability and scalability to efficiency and accuracy, all these benefits make an expert system a powerful application.
So, want to make a career in the field of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)?
Then, enhance your skills in AI with the course MCA (Specialization: Artificial Intelligence) offered by Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham (Amrita AHEAD) through Jaro Education. This course helps students acquire an in-depth knowledge of Artificial Learning (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) by implementing related problems in a variety of applications, such as IoT and computer vision.
Frequently Asked Questions
In Artificial Intelligence, an expert system is a knowledge-based system that is required to solve complex problems and provide decision-making abilities to find accurate solutions as human experts.
Yes, courses available for expert systems in AI are helpful as they can provide you with a valuable understanding of the same. The courses also support finding relevant jobs and practical training required in today’s fast-moving world.
Designed to help users solve complex issues in any specific domain, the roles of an expert system include:
- Decision-making
- Knowledge Representation
- Diagnosis and Troubleshooting
- Financial Advisory
- Supporting Human Decisions
- Inference Engines
One of the best examples of applications of expert systems in Artificial Intelligence is Medical Diagnosis. Through this application, expert systems help doctors and nurses diagnose severe diseases, recommend treatment options and monitor patient’s health conditions. For instance, MYCIN is a backward chaining expert system that was designed to identify bacterial infections, like bacteraemia and meningitis, recommend antibiotics and suggest treatment.
Expert systems are used in the education sector to help students with the learning process. AI and expert systems help solve problems by using data from the generated knowledge base. With the process, expert systems help the students on the basis of knowledge.
Medical diagnosis was the initial application where expert systems were used. Other applications of expert systems in Artificial Intelligence are planning and scheduling, finance domain, knowledge domain, and designing and manufacturing domain.
Generally, expert systems include four components – knowledge base, user interface, inference engine and explanation systems.
The limitations of expert systems in AI include:
- Cost-effective
- Maintenance costs
- Development costs
- Requires constant manual updates
- Follows only specific domains
- Lack of logic behind the decisions
The best language used for expert systems is Prolog which has an indicative programming style and a powerful design-matching facility.
The main characteristics of expert systems in AI include high performance, reliability, understandable and highly responsive.
Whether it’s healthcare, finance or human resources, the applications of expert systems in Artificial Intelligence are used everywhere. Expert systems are crucial for these domains because they help organisations with improved decision-making, reliability, scalability, increased efficiency, cost-effectiveness and enhanced accessibility.
An expert system is a computer-based program in Artificial Intelligence that is designed to solve difficult problems in a particular domain like humans. The data stored in the knowledge base is provided by domain experts.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a machine or a computer program that thinks, learns and reacts like humans and uses methods based on humans’ behaviour to resolve complex problems, while expert systems are computer programs that are designed to solve complex decision-making problems.
Google may use expert systems for particular problems within the organisation, especially in areas where specialised knowledge or decision-making is required. However, the Google search engine more depends on complex algorithms and AI models than on expert systems.
To improve the accuracy of your expert system, you must consider the following ways:
- Select an appropriate domain
- Gather and authenticate data
- Create the knowledge base
- Execute the inference engine
- Improve the explanation systems
- Analyse and update the expert system.












