Types of Models of organizational behavior
Table of Contents

- jaro Education
- 20, July 2024
- 5:00 pm
Isn’t it interesting how some teams do exceptionally well, while others fail? Or how certain leaders can install an innovative spirit while others cannot even inspire their teams? That makes for learning the types of organizational behavior.
The concept of organizational behavior is how the individuals and the group norms dictate their behavior in an organization and how to handle all that behavior for success. While some of the knowledge areas included in the models of OB are manager/employee skills, an aspiring business leader must read OB to learn about the critical factors: motivation, leadership, communication, and team dynamics since these influences are at the workplace.
In fact, this is what makes it more exciting, as organizational behavior is not a theory; it is also very much about what can be learned and used right now to produce a good, productive, and, most importantly, transforming the culture of your organization.
So, what are you waiting for? Dive right into the dynamic world to discover how you can unfold the maximum potential of your team. Let’s start exploring!

What is Organizational Behavior?
Organizational behavior is the study of how employees interact within groups in a workplace. It focuses on understanding and managing these interactions to improve productivity, job satisfaction, and overall workplace effectiveness. It’s an effective interface between human behavior and the organization itself.
Managers and human resource professionals can evaluate and predict the effectiveness of policies they have in place. It works from both the standpoints- for the company’s growth as well as employee’s well-being.
The Levels of Study of Organizational Behavior
The study of types of organizational behavior is conducted on three levels- the individual, group, and organizational levels. Before understanding the models of organizational behavior, leaders must know the key components and metrics of studying organizational behavior. These are:
*killerinsideme.com
1. Individual behavior
- Personality: Understanding how individual differences in personality can affect behavior.
- Perception: How individuals interpret and make sense of their environment in an organization.
- Motivation: Theories and practices that influence what drives people to act.
- Learning: How individuals acquire new knowledge and skills.
2. Group behavior
- Team Dynamics: How employees interact and collaborate to work together in groups.
- Communication: It encompasses how effective and fruitful the information exchange is within the organizational groups.
- Leadership: Styles, traits, and behaviors of employees that influence others.
- Conflict and Negotiation: It focuses on managing disagreements, if any, and finding solutions that benefit everyone in the group.
3. Organizational Structure
- Organizational Design: How jobs and tasks are formally divided, grouped, and coordinated.
- Culture: Shared values, beliefs, and norms influence people’s behavior.
- Change Management: Processes for successfully implementing organizational changes.
- Work Environment: Physical and psychological conditions of the workplace.
4. External Environment
- Economic Factors: How economic conditions impact organizational behavior.
- Technological Changes: Influence of new technologies on organizational processes and employees productivity.
- Globalization: Long and short-term effects of operating in a global marketplace
Understanding Different Types of Organizational Behavior
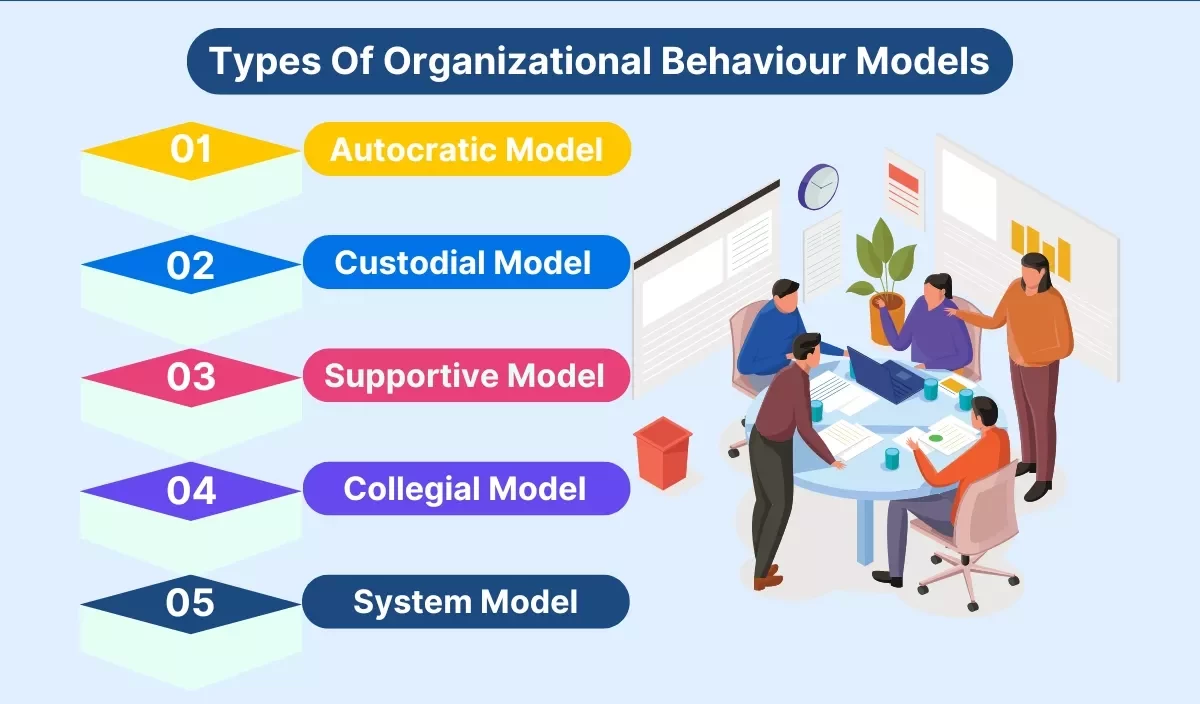
Various models of OB have been developed to explain, predict, and influence behavior within organizations. These models of OB help managers understand employees’ peer-to-peer interaction and the organizational structure. These are:
*UnStop
1. Autocratic Mode
The autocratic model of organizational behavior is characterized by a top-down approach where authority is centralized. Managers hold the power, and employees are expected to follow instructions without question. This model is often based on the traditional belief that people are inherently lazy and must be pushed to work.
Characteristics of an autocratic model include:
- Authority: Centralised power and decision-making.
- Control: Strict supervision and control over employees.
- Motivation: Employees are motivated by fear and discipline.
- Communication: One-way communication from top to bottom.
Notable Advantages of the Autocratic Model are:
- Quick decision-making as authority is concentrated at the top.
- Clear and direct communication/disclosure of policies and procedures.
2. Custodial Model
The custodial model is one of the types of organizational behavior that focuses on the organization’s economic resources. It aims to provide security and benefits to employees to ensure loyalty and commitment. This model arose as a response to the limitations of the autocratic model, emphasizing the welfare of employees.
Characteristics of the Custodial Model are:
- Economic Security: Emphasis on providing job security, fringe benefits, and incentives.
- Dependence: Employees become dependent on the organization for their economic security.
- Motivation: Employees are motivated by financial rewards and security.
Advantages of Custodial Model include:
- Increased job security and employee satisfaction.
- Reduction in labor turnover and absenteeism.
3. Supportive Model
As the name suggests, the supportive model is mainly based on leadership and employee support. It focuses on the role of managers, HRs, and leaderships. They all work towards supporting their employees and enhancing their skills. It ultimately helps foster a positive working environment in the organization.
Characteristics of a Supportive Model include:
- Leadership: Managers act as coaches and mentors.
- Employee Development: Focus on training and development.
- Motivation: Employees are motivated by recognition and job satisfaction.
- Communication: Two-way communication is encouraged.
The advantages of a Supportive Model are:
- High employee morale and job satisfaction.
- Employees are encouraged to be more innovative and creative.
- Build strong leader-employee relationships in the workplace.
Limitations of a Supportive Model are:
- A significant investment is required for the training and development of employees.
- This model may be ineffective in large-scale organizations.
- Managers need to be highly skilled in leadership and interpersonal skills.
4. Collegial Model
The collegial model is based on partnership and teamwork. It promotes community building and collaboration within the organization. Employees and managers can work together, getting equal opportunities and recognition.
Characteristics of a Collegial Model include:
- Teamwork: Emphasis on collaborative efforts and team-based activities.
- Participation: Employees participate in decision-making processes.
- Motivation: Driven by shared goals and mutual respect.
The advantages of the Collegial Model are:
- High levels of employee engagement and commitment.
- Fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility among employees.
- Promotes creativity and innovation through collaborative efforts.
The pitfalls of a Collegial Model are:
- Decision-making can be slower due to the need for consensus.
- Potential for conflicts if team dynamics are not managed effectively.
- It is based on a culture of trust and mutual respect, which can be difficult to develop.
5. System Model
In a system model, the organization is considered an open system. It focuses on different subsystems which are working interdependently. These include employees, managers, technology, and the entire environment.
Characteristics of a System Model include:
- Holistic View: Considers the organization as a whole, including external factors.
- Interdependence: Focus on the interrelatedness of different organizational components.
- Adaptability: Emphasizes the need for flexibility and adaptability.
The advantages of a System Model are:
- Comprehensive understanding of organizational dynamics.
- It promotes continuous improvement and innovation among employees.
The drawbacks of the System Model are:
- Complexity in managing and understanding all interrelated components.
- Requires regular monitoring and adjustments depending on the current challenges.
- This model can be resource-intensive.
Significance of Types of Models of Organizational Behavior
Comprehending the types of models of organizational behavior is crucial for managers and highly beneficial for employees. Managers can spot the traits of their employees depending on which they can enhance their skills and work on their well-being. Some notable features of models of organizational behavior include:
| 1. Enhancing Managerial Effectiveness | This behavioral study equips managers and leaders with the knowledge to assess and predict employee behavior. This understanding helps them to prepare effective strategies to motivate their employees. It also helps them build better leadership skills. Being a manager, you can build an environment for your employees and encourage them to develop their skills. Employees feel valued, supported, and satisfied working in such an environment. |
| 2. Promoting a Positive Organizational Culture | These models of OB are the foundation of curating the organizational culture as they promote teamwork, mutual respect, and support. For example, the collegial model promotes a culture of shared responsibility and a collaborative environment. It helps create a sense of working in a single team. |
| 3. Facilitating Change Management | Studying and implementing these tools in real-life scenarios helps bring effective organizational changes. Managers can easily figure out how changes brought in one unit of the organization can affect the entire working system. This model is usually followed during mergers, and managers can easily plan for upcoming changes. |
| 4.Enhancing Organizational Performance | By applying the principles of different organizational behavior models, organizations can improve overall performance. For example, the supportive and collegial models of OB focus on employee engagement and participation. By employees’ engagement in important opinions, managers can choose better business ideas. Such decision-making processes can lead to innovative solutions. |
| 5. Personal Development and Leadership | For professionals aspiring to be in leadership roles, understanding these models of OB is essential for personal development. They provide a foundation for developing effective leadership styles that are adaptive to various organizational contexts. By gaining these insights, a leader can build trust with their employees. Not only can it inspire the employees, but also help them be productive. |
Why Symbiosis Online MBA To Accelerate Your Career?
The online MBA Degree Programme at Symbiosis School for Online and Digital Learning (SSODL) is the course for those wanting to hone strategic intelligence and surely expect a significant career in the corporate world.
This programme truly promises to empower potential learners with the skills to become effective contemporary leaders in an increasingly fast-moving business environment. Learn at a world-class institution, develop the knowledge and skills that make a professional stand out globally in times when the going gets hard. Curriculum designed by top B-School experts of Symbiosis and taught by competent faculty ensures that students receive the best education quality.
The disciplines would include Marketing, HR, Finance, Operations, Business Analytics, International Business, Hospital and Healthcare Management, Agri Operations Management, and Logistics and Supply Chain Management. Advance further towards professional growth, garner skills and knowledge which is in demand in today’s job market, and realize your career aspirations.
Programme Highlights:
- Council for Online Degree Programme by Symbiosis equally recognized online-assessment
- 100% Online degree programmes without campus visits
- Online evaluations in accordance with UGC guidelines project
- 24*7 access to the Learning Management System degree program
- Curriculum designed by experts from Top Ten Symbiosis Institutes, India icon
- Access to Recorded Sessions- Learn at your own pace icon
- Live Interactions with Faculty online class
- Peer to Peer Doubt Sharing & Solving Sessions
Eligibility:
To qualify for the course, the applicant should have obtained a degree from any of the recognized universities/institutions of national importance with at least 50% marks or its equivalent graduation level.
Explore More About Symbiosis:
Symbiosis School for Online and Digital Learning (SSODL) offers certificate and degree programs at UG and PG levels in an online mode. Under the auspices of Symbiosis International (Deemed University) (SIU), these programs are UGC and AICTE-recognized so that the level of rigor, great faculty, and learner-centered education combined with the regular classroom programs of Symbiosis are not compromised. The course content is conducted in a self-paced format; therefore, it not only offers flexibility but covers areas such as Business, Technology, Humanities, and much-celebrated healthcare programs, creating graduates who are endowed with both leadership qualities and intellectual depth.
How Does Jaro Aid Your Growth?
Jaro Education is the most trusted online higher education in India. With strong domain expertise and a deep insight into executive education, Jaro Education has transformed directly more than 3.50 lakh professionals in the last 15+ years through its 23+ learning centers in India, Singapore & USA. The company aims to foster entrepreneurs & working professionals from entry-level to C-Suite level in every field and industry by providing executive education programs relevant to their needs. Jaro Education’s transformation of the online education landscape in India is something that is well known, and it offers over 150+ management, technology, and techno-functional programs in collaboration with the top reputable institutes.
Final Thoughts
It’s vital to understand the types of models of organizational behavior for managers. However, times have changed, and so have how employees work in a dynamic and hybrid environment. That said, managers and leaders must follow either a single or a combination of the models of OB depending on several factors. They must consider the organization’s goals, culture, and external environment. Modern organizations are adopting a combination of these models of OB to create a dynamic and flexible approach.
Frequently Asked Questions
Organizational behavior could be defined as a study that examines how an individual and a group behave inside an organization; this includes putting under investigation factors such as motivation, leadership, teamwork, communication, and even organizational culture that affect the internal functioning of an organization.
The main models of organizational behavior can be coded as follows:
- Autocratic Model- This is the kind of model that will represent power and authority; employees should obey the instructions of leaders.
- Custodial Model- This model is adopted when security and benefits increase employee motivation towards making them dependent.
- Supportive Model- This model demonstrates employee motivation by leadership; managers guide employees positively to improve performance.
- Collegial Model- Organization between employees and management is encouraged to give an impression of partnership and collective responsibility.
- System Model- This concerns how the organization is seen, namely, as a system with other smaller interrelated parts, focusing on feedback and change with the outside world.
These models of OB will help businesses determine relationships regarding human behavior at work, which will further improve management practices, motivation, productivity, and health in the organizational culture.
Autocratic model: In this environment, the climate is highly centralized, and employees would only follow the orders because they do not have any doubt that they will come across fear and power as motivational values.
The Custodial Model defines loyalty and motivation from benefits and security for employees rather than from fear.









