How To Select The Right Forecasting Technique?
Table of Contents

- jaro Education
- 11, August 2024
- 5:30 pm
Being proactive is crucial in the rapidly evolving manufacturing industry. Among various steps toward this, accurate forecasting plays a vital role. A successful technique in forecasting allows the manager to predict the trends in the market, properly allocate resources, and make decisions, among many other benefits. Now, in such a wide sea of methods and techniques, how can you tell which one is the right way? This blog delves into the details of various types of forecasts and the alternatives in methods, comprehensively helping manufacturing managers make a choice.
For those who want to go a little deeper into the forecasting side and want to know a bit more on the manufacturing management front, you get a thorough understanding of the Post Graduate Certificate Programme in Manufacturing Management & Analytics provided by the IIM Tiruchirappalli.
A Comprehensive Guide to Forecasting Techniques
1. A Review of Forecasting Techniques
Forecasting is an estimate of some future events based on knowledge of past events and analysis. Forecasting in the subject of manufacturing management is quite strategic since demand, production planning, and inventory are the periphery of success.
2. Qualitative Forecasting Techniques
The qualitative forecasting technique involves judgements and opinions rather than numerical data. These methods are particularly used when historical data is of little value or the activity is new, for instance, the launching of a new product.
3. Delphi Method
The Delphi approach in forecasting methods is one in which a panel of experts provide their forecasts independently of what the others have to say. These forecasts are then aggregated, and finally, the panel settles the forecast through repeated rounds of discussions. This approach is less influenced by any particular dominant person; hence, it provides a wholesome forecast.
4. Market Research
Market research involves obtaining relevant information from the potential customers or population by using tools like surveys, interviews, focus groups, etc. Furthermore, this data significantly contributes to understanding customer tastes and preferences for newly launched products.
5. Quantitative Forecasting Methods
In quantitative forecasting techniques, one can predict future events through the use of statistics or numerical data. These techniques have, however, been considered more accurate than many of those in the first group.
6. Time Series Analysis
Time series analysis is the examination of historical data points to identify trends and patterns. Moving averages, exponential smoothing, and the application of ARIMA models are very common forecasting methods for time series analysis.
7. Causal Models
Causal models are sometimes called econometric models. They examine the relationships among variables and establish cause-and-effect relationships. For instance, one likely would use a causal model to discover how changes in economic variables such as gross domestic product or unemployment rates impact demand for a product.
Choosing the Right Forecasting Technique
An appropriate forecasting method depends on many factors: the nature of the data, the time horizon, and the needs of the organisation. It determines the accuracy and power required of the techniques and hence governs selection, as mentioned in a report by Harvard Business Review.
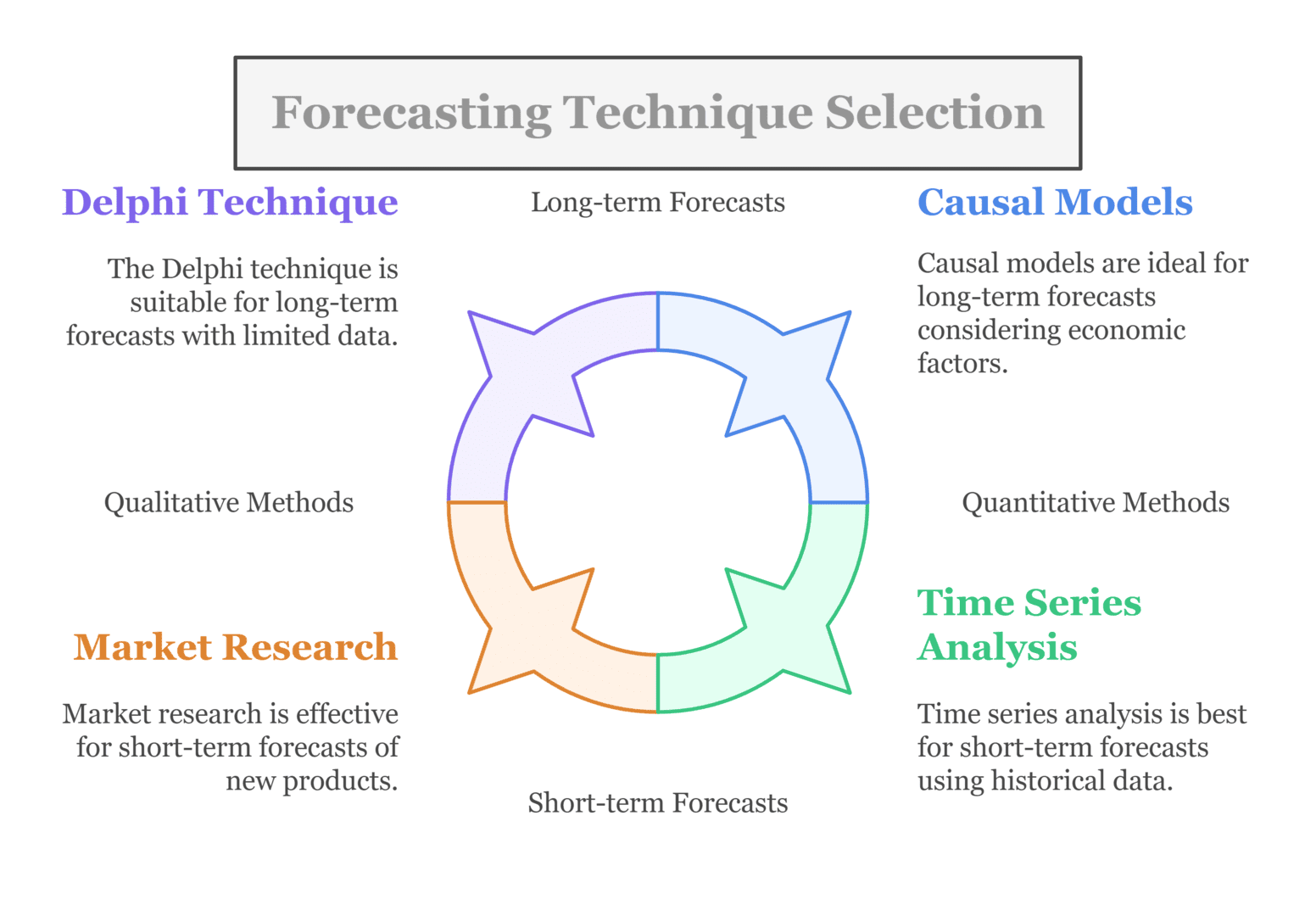
- Nature of Data
The nature and quality of available data greatly influence the selection of the type of forecasting technique to be used. If you have a long history of data, quantitative methods such as time series or causal models are appropriate. However, when data are limited, one may resort to qualitative methods like the Delphi technique or marketing research.
- Time Horizon
The time horizon of the forecasting technique also serves to play a vital role. Short-term forecasts (up to one year) usually focus on immediate trends and patterns; hence, they are based on time series analysis. Long-term forecasts (beyond one year) usually base their negotiations on causal models to account for the economic factors that bring a broad objective to the markets.
- Specific Needs of the Organization
Think about which approach is better suited to the unique requirements of your organisation. Market research might be the best solution if you need to make projections for demand for a newly released product. Time-series analysis is a better way to go if the more important thing is ensuring the optimal level of inventory based on historical sales information.
- Combining Forecasting Methods
In some cases, the union of many different forecasting techniques can give a much more accurate answer than anyone can do alone. This approach is a composite or ensemble method of forecasting in general—a forecasting method in which the better parts of each can be synthesised to give a better overall feel for the prediction.
For example, a manufacturing manager can use time series analysis to forecast short-term demand and then combine it with some market research insights, say imminent changes in customers’ preferences, to supplement the previous portion of his prediction.
What Is Sale Forecasting?
Forecasting sales is an art that helps the organisation estimate the total revenue or count of deals that it will be able to close in the future based on prior data.
organisation
Sales organisations integrate private historical data, applicable public economic metrics, and historical patterns to get a glimpse of broader or narrower forecasts of a company’s possibilities. Forecasts serve as benchmarks for months, quarters, or years, and they may also serve as components in team commission calculations.
Forecasting can be understood as one of the most fundamental top-tier areas in business analytics. This is because the sales forecast forms the basis for developing strategies for building new business associates, sending to targeted accounts, and estimating replenishment needs for shopfronts in the geographic context.
Facts form the basis of sales forecasting, but uncertainty and risk also contribute to the overall figure. This is because uncertainty is, well, uncertain, and the imagined effects of risk-taking are not wholly predictable as well; it is better to always bear in mind that a forecast may not come true a hundred per cent. But it is always better to have an umbrella handy and leave it unused than be caught in a sudden downpour without it.
What Are The Types Of Sales Forecasting Methods?
Data alone is the raw material referred to; one may just face sales depending on the techniques applied in forecasting. Different forecasting techniques can be used according to what information is being valued from the given sales figures; one could use internal or external factors for businesses. However, those expressions can mainly be entered into two general forecasts, which are:
- Qualitative sales forecasting: The intangible qualities that turn into potential sales and income are predicted through the opinion, judgement, and insight of an expert.
- Quantitative sales forecasting: This method, while forecasting future revenue, depends heavily on the performance figures and historical developments of sales and income.
How Do You Select An Appropriate Sales Forecasting Technique?
All sales forecasting methodologies outlined above are for answering the question: “What performance can one expect from sales in a given period?”
Regardless of the model you select, follow these steps to use it effectively:
Step 1: Define Your Plan
Clearly state the problem and what the forecast information will be used for, identify for whom the findings will be intended, and decide how responsibilities will be allocated for carrying out the forecasting project.
Step 2: Gather materials
It should contain relevant data, information from your CRM, and tools you may need to complete your chosen sales forecasting model.
Step 3: Conduct a preliminary analysis
What will be your expected results for this forecast? Consider some relevant things like seasonality, as you will compare your expectations later with the result. Consider also the pros and cons of that particular sales forecast method you are using and how this may influence your view about its prediction.
Step 4: Use your sales forecasting model
Run your model and look for an output. The output must follow logically from the question you asked. If not, debug it and run it again. Be sure to document results from each run as redundancy precautions.
Step 5: Time to evaluate the outcome
Did the information produced through the sales forecasting method make sense in your expectations or the lack thereof? In case this output data came to fruition, how would it affect the activities of your sales team moving forward?
Practical Application in Manufacturing Management
Now, let’s take the example of one manufacturing company that manufactures consumer electronics. Let’s assume that this case pertains to predicting the demand for a new smartphone model.
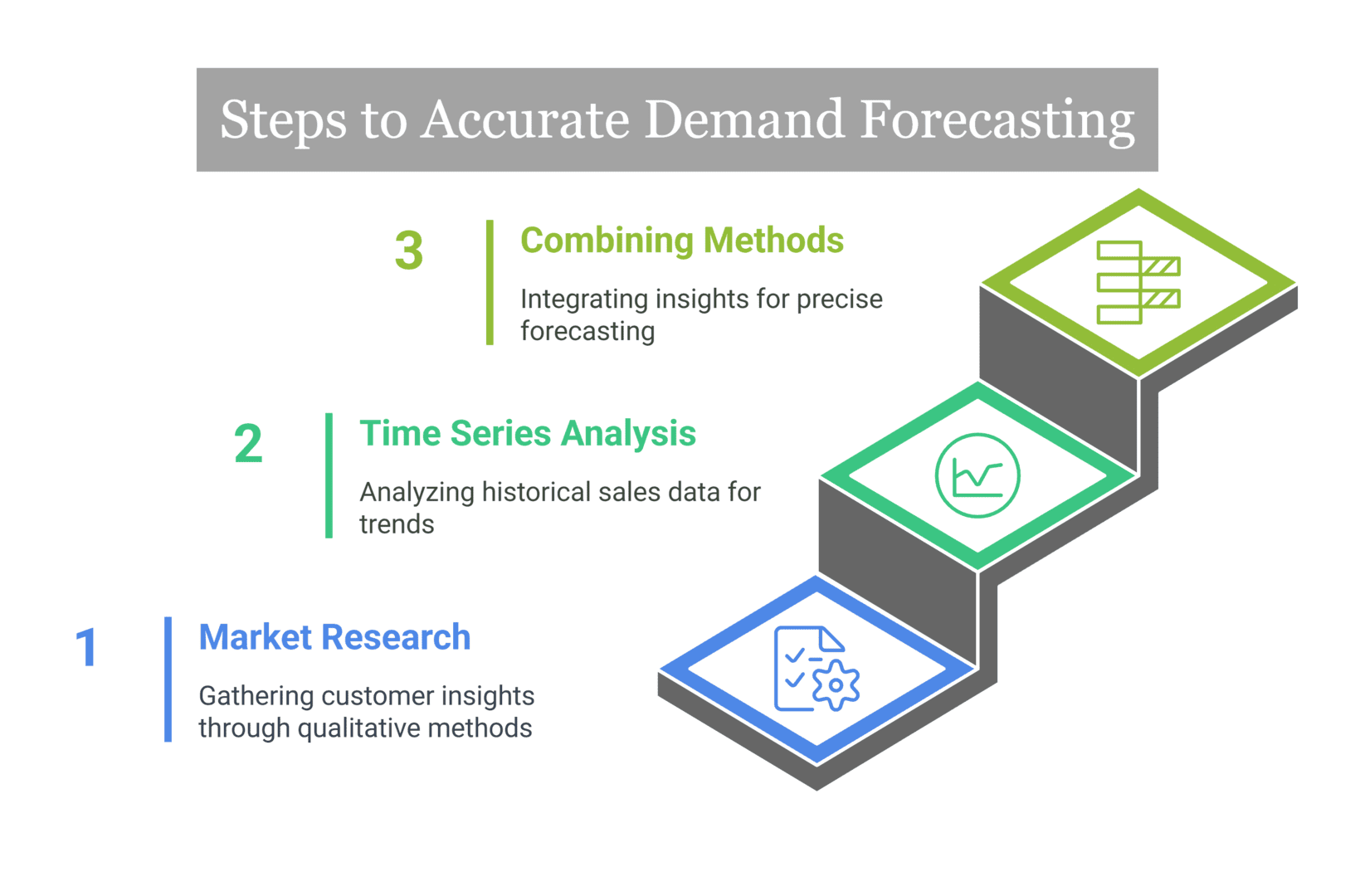
Step 1: Market Research
The firm will have undertaken market research and will have gathered customer knowledge in terms of those who associate with features, price points, and the intent to purchase. The firm will learn and understand the initial demand for the new smartphone model through the qualitative data it has collected.
Step 2: Time Series Analysis
Next, time series analysis is used to analyse historical sales data for previous smartphone models. Using a quantitative technique, the analysis can identify trends and patterns, which can be used for guiding the forecast of the demand for the new model.
Step 3: Combining Methods
By incorporating qualitative market research insights along with historical quantitative data analysis, a more comparatively accurate forecast can be determined. This composite approach is important for the company in planning its production, managing inventory, and allocating resources correctly.
What Is Business Forecasting?
Regardless of whether the specifics are related to a business, such as sales growth, or forecasts for the economic environment, business forecasting techniques consists of making informed guesses for certain business metrics. With uncertain economic conditions, business and operational decisions are made based on the predictions of how the world will be.
Key Takeaways:
- Forecasting is important to businesses so that they may make informed business decisions.
- A financial forecast is an informed guess at best that is dependent on methodology and past information that may not capture some variables.
- Forecasting models may be qualitative, and they may also be quantitative.
What Are The Types Of Business Forecasting Methods?
Two chief types of business forecasts are qualitative models and quantitative models.
1. Qualitative Models
Qualitative models have traditionally prospered in short-term forecasting, where the extent of the forecast was limited. Qualitative forecasts are expert-orientated, as market mavens or some other subset of the market need to weigh in with an informed consensus.
- Qualitative models can predict the short-term performance of companies, products, or services, but, simply due to their dependencies on opinion, they can be limited. Qualitative methods include:
- Market research: Polling large numbers of people on a certain product or service as a prediction of how many will eventually buy or use it once it is launched.
- Delphi method: This involves consulting experts in the field to get general opinions, which are then compiled into a forecast.
2. Quantitative Models
Quantitative models reject the expert and try to do away with humans altogether. These approaches concentrate purely on data, thereby avoiding the whims of the people behind the numbers. The approaches also try to predict where, in months or years, variables like sales, gross domestic product, housing prices, and so on will be. Quantitative includes the indicator approach, which is premised on the unchanged relationship of certain indicators, that is, in our case, between GDP and the unemployment rate, relatively unchanged over time.
By following the relationships and then following the leading indicators, you can estimate the performance of the lagging indicators by using leading indicator data.
- Econometric modelling: This technique is a more mathematically rigorous version of the indicator approach. Econometric modelling avoids assuming that relationships remain the same but rather tests for the internal consistency of data over time and the significance or strength of the relationship between data sets. Econometric modelling applies to making custom indicators for more targeted activities. However, typically, econometric models are conducted in academic fields to assess economic policies.
- Time series techniques: In time series, past data becomes the criterion for predicting future events. This technique differs from one time series methodology to the next, depending on the details, such as incurring more weight for recent data or discounting certain outlier points. The forecaster wishes that by monitoring what occurred in the past, he will get at least a better-than-average view of the future. It is one of the most common forms of business forecasting techniques, as it is cheap and crowds many other methodologies.
Impact of Forecasting Methods on Business Growth
| Advanced Forecasting Techniques | Organisations that require more complex forecasting techniques have various advanced solutions at their disposal, including machine learning and artificial intelligence. |
| Machine Learning | Machine learning algorithms can analyse, identify, and predict highly complex patterns based on large data sets using regression analysis, neural networks, and decision tree techniques. Some common forecasting methods in machine learning include regression analysis, neural networks, and decision tree techniques. |
| Artificial Intelligence | AI-powered forecasting systems can continuously learn and adapt to new data, improving their accuracy over time. These systems can handle complex scenarios, such as predicting the impact of external factors like economic shifts or competitor actions on demand. |
How To Learn Forecasting Techniques In Depth?
About IIM Trichy
IIM Tiruchirappalli (IIMT) is one of the fastest-growing generational IIMs and now houses state-of-the-art campus facilities covering 174 acres. Since its establishment in 2011, the Institute has successfully established itself as a top-tier management institution, renowned for its ability to generate and share management knowledge. The Higher Education Forum (HEF) awarded IIM Tiruchirappalli with the Leadership & Innovation Award: 2020 in the Business School Category at the 11th HEF Annual Convention. In the Outlook-ICARE India MBA Rankings 2020, the institute ranked seventh among such top B-schools. The National Institutional Ranking Framework, Ministry of Human Resource Development, Government of India (2023), awarded IIM Tiruchirappalli a rank of 22 among management institutions. The e-Learning Centre of Executive Education and Consultancy (EEC) extends further into the mission of IIMT by reaching out to aspiring executives, keeping in mind their limitations of time and space. Thus, the e-learning programmes enable IIMT to enter the online executive education space, focusing on delivering quality management education that is both contemporary and affordable.
Programme Overview:
Typically, manufacturing is considered a complex system because of the interacting processes. The activities and resources of these processes generate data in huge volumes that are hardly captured or effectively utilised. With the development and emphasis on analytics, it has become imperative to derive insights from this data for informed decision-making at a micro and macro level. Executives in manufacturing industries must quickly adapt and respond to these challenges in a tailored manner.
Befriend the upcoming growth path through the Post Graduate Certificate Programme in Manufacturing Management and Analytics offered by IIM Tiruchirappalli. This interdisciplinary programme is geared towards equipping professionals with fundamental concepts, techniques, and tools for managing manufacturing systems with analytics in a very practical way. The program will also help participants deal with quantitative reasoning and gain insights to strengthen their planning, increase production efficiencies and yield, and enhance performance into the future, thus benefiting the bottom line, thanks to hands-on exercises, practical applications, and case studies.
In addition, the schedule for the program is written and arranged such that the weekend classes are fitting for the poor timing of working professionals.
Admission Requirements
Eligibility requirements include:
- A Bachelor’s Degree with a minimum of 50% marks or CGPA equivalent (45% for SC/ST/PWD candidates) from a recognized university;
- An equivalent qualification recognized by the Ministry of HRD, Government of India;
- The candidate must have a minimum of 1 year of post-qualification experience.
- Reservations will be available to eligible candidates in accordance with Government of India norms.
Explore Career Opportunities Under Jaro Education Guidance?
Beginning in October 2023, Jaro Education has had in-depth knowledge of the executive education market for more than 15 years and has greatly enhanced the careers of 300,000-plus professionals through 23 learning centres across the country, Singapore, and the USA. Jaro wants to cultivate entrepreneurs and working professionals from entry-level positions to the C-suite in every field and industry by developing executive education programmes for their needs. Considered to have changed the face of online education in India, Jaro Education also offers 150-plus master’s, technology, and techno-functional programmes with leading reputed institutes.
Are you ready to accelerate your career?
Conclusion
Manufacturing managers consider the selection of the right forecasting technique to be of vital importance. Understanding the different forecasting techniques available increases the value of the manager’s selection decision-making. Whether it is qualitative techniques such as the Delphi model and market research or quantitative approaches like time series analysis and causal models– each technique has its strengths and its related fields of application.
Frequently Asked Questions
A sales forecast is the process of estimating future sales for a product or service over a specific time. The forecast is typically done using historical data, market trends, and other relevant factors to predict how much product or service will be sold, helping businesses plan their resources and make informed decisions.
Sales forecasting is essential because it helps businesses manage resources, set realistic goals, plan production, make budget allocations, and determine cash flow requirements. Accurate sales forecasting can also provide insights into market trends and customer behavior— both of which aid strategic decision-making.
The most common sales forecasting methods include:
- Qualitative Methods: These rely on subjective judgements, market research, and expert opinions, often used when there’s limited historical data or for new products.
- Sales Force Composite: Involves input from salespeople to estimate future sales.
- Delphi Method: A group of experts independently forecasts sales, and their feedback is consolidated to create a final estimate.
- Market Research: Collect data from potential customers to predict future sales.
- Quantitative Methods: These use historical data and mathematical models to predict future sales.
- Time Series Analysis: Uses historical sales data to predict future trends, often involving moving averages or exponential smoothing.
- Causal Models: Relies on identifying relationships between sales and external factors (e.g., advertising spend, market conditions) to predict future sales.
- Qualitative forecasting relies on subjective data and expert opinion and is often used when there is little to no historical data or for new products and services.
- Quantitative forecasting uses historical data and statistical methods to predict future sales, making it more objective and reliable, especially for established products.
The right method depends on the type of product, the amount of historical data available, and the level of accuracy needed:
- If the product is new or in a rapidly changing market, qualitative methods like sales force composite or market research may be more effective.
- For established products with sufficient historical data, quantitative methods such as time series analysis or causal models are more appropriate.









