Insightful article on enterprise software development! The breakdown of trends and benefits is highly informative. Thanks for sharing this valuable content!
Enterprise Software Development: The Ultimate Guide for Modern Businesses
Table of Contents

- jaro education
- 25, November 2024
- 3:00 pm
Ever wondered how large organizations efficiently manage their operations, workflows, and customer interactions? The answer lies in Enterprise Software Development, the backbone of streamlined processes and effective decision-making. Let’s dive deep into this transformative domain and see how it powers businesses to scale and thrive.
What Is Enterprise Software?
Enterprise software refers to applications designed to address the specific needs of organizations, helping them operate smoothly across various functions like HR, finance, supply chain, and customer relationship management (CRM). Unlike regular consumer software, enterprise software focuses on scalability, reliability, and integration across diverse systems.
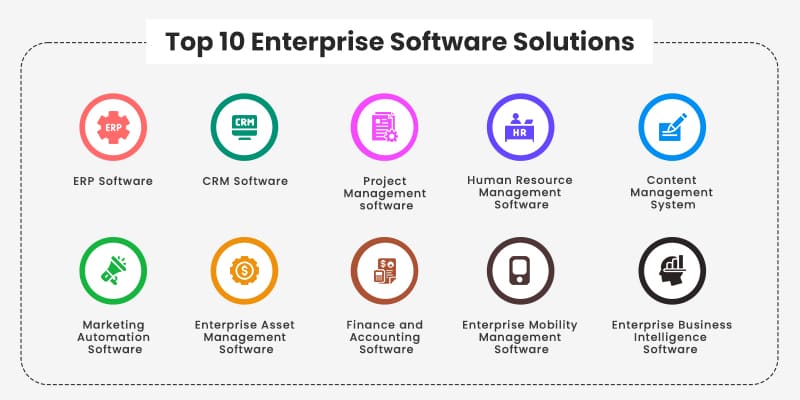
*Matellio
Some common enterprise software examples include:
| Software Type | Enterprise Software Examples | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) | SAP, Oracle ERP | Integrates business processes and data. |
| Customer Relationship Management (CRM) | Salesforce, Zoho CRM | Manages customer interactions and sales. |
| Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS) | Workday, BambooHR | Handles HR tasks like payroll and hiring. |
| Supply Chain Management (SCM) | Kinaxis, Logility | Optimizes logistics and supply chain flows. |
These tools fall under the umbrella of enterprise applications, offering tailored solutions for large-scale operations.
Why Enterprise Software Development Matters
The demand for enterprise software development arises from the unique challenges businesses face. Companies need systems that are robust, secure, and capable of handling vast amounts of data while ensuring seamless collaboration across departments.
Organizations often turn to enterprise software development services to build customized solutions. These services include designing, developing, and maintaining enterprise-grade software that aligns with an organization’s specific goals.
Key Features of Enterprise Software Applications
When we talk about enterprise software applications, their distinguishing features set them apart from standard software. Here are some of their key attributes:
1. Scalability
Designed to grow with the organization, enterprise software must accommodate increased users, data, and functionalities without a hitch.
2. Integration
These applications often integrate with other tools, ensuring a smooth flow of information across platforms like ERPs, CRMs, and analytics systems.
3. Customization
Off-the-shelf solutions may not always fit; hence customization becomes crucial to meet specific organizational needs.
4. Security
With sensitive data at stake, enterprise software prioritizes robust security measures to prevent breaches and ensure compliance.
5. Analytics and Reporting
Advanced reporting tools allow businesses to make data-driven decisions, fostering growth and efficiency.
Enterprise Software Development Services
Building enterprise-grade software is no small feat. It involves a mix of technology, strategy, and industry expertise. Here’s a closer look at some common enterprise software development services:
1. Custom Software Development
This involves designing and building software tailored specifically to an organization’s needs. Examples include internal communication platforms or a bespoke inventory management system.
2. Software Integration
This involves designing and building software tailored specifically to an organization’s needs. Examples include internal communication platforms or a bespoke inventory management system.
3. Cloud-Based Solutions
With cloud technology gaining traction, many businesses opt for enterprise applications hosted on platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
4. Mobile Enterprise Apps
Mobile-friendly applications ensure employees can access critical systems from anywhere, enhancing flexibility and productivity.
5. Maintenance and Upgrades
Regular updates and proactive maintenance are vital to keeping the software efficient, secure, and relevant in the fast-changing tech landscape.
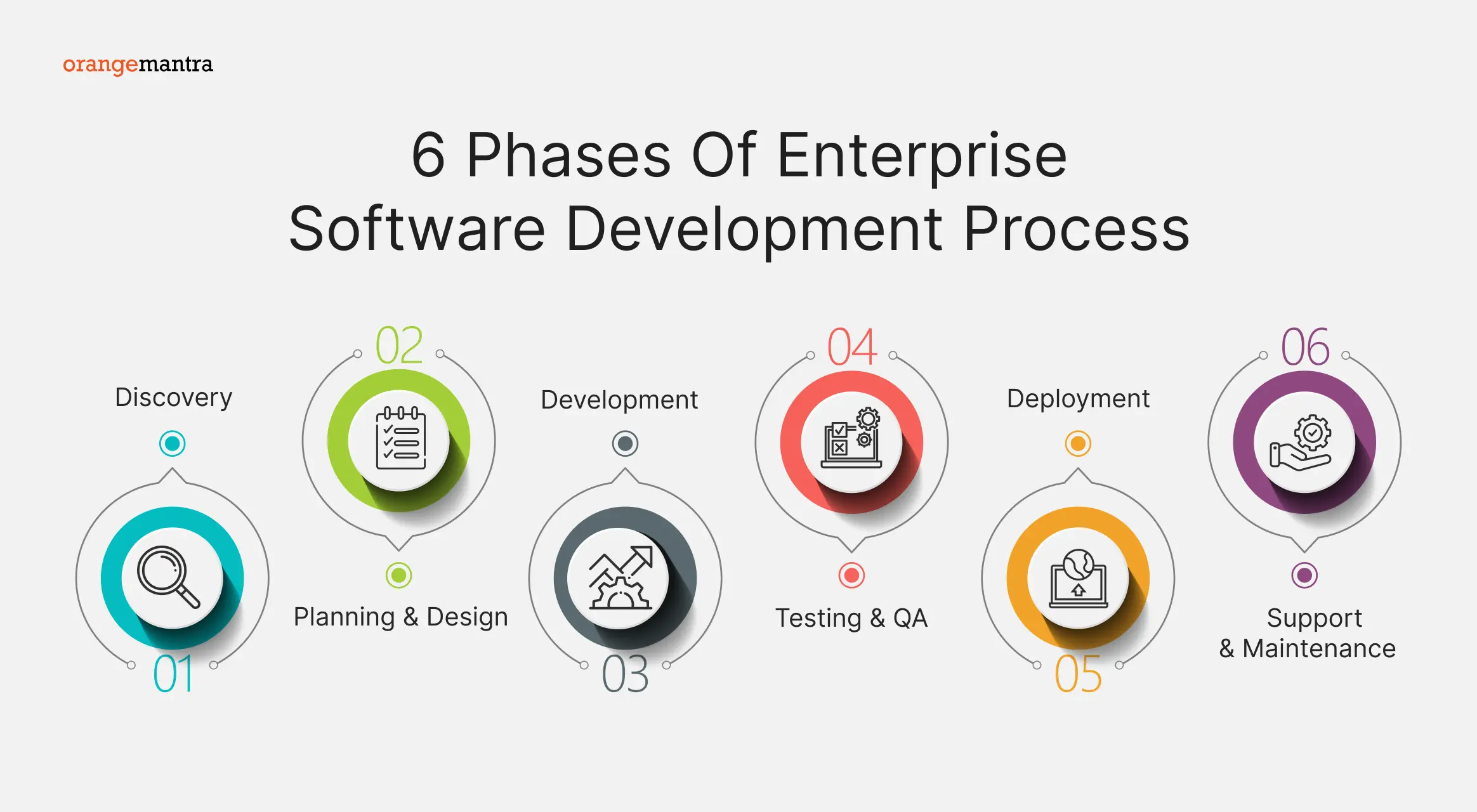
*OrangeMantra
Enterprise Software Development Best Practices
To create software that aligns with business objectives and delivers real value, adhering to enterprise software development best practices is essential.
| Why It Matters | Best Practice |
|---|---|
| Understand User Needs | Ensures the software aligns with actual business requirements, avoiding costly misalignment. |
| Adopt Agile Methodologies | Enables iterative development, fostering flexibility and collaboration throughout the project. |
| Focus on Security | Protects sensitive data and ensures compliance with industry regulations like GDPR or HIPAA. |
| Plan for Scalability | Allows the software to grow with the organization, avoiding costly redevelopments later. |
| Thorough Testing | Prevents bugs and ensures smooth performance in real-world scenarios. |
| Choose the Right Technology Stack | Impacts software performance, maintainability, and compatibility with existing systems. |
Enterprise Applications: Real-World Examples
To truly grasp the impact of enterprise applications, let’s look at some real-world scenarios:
Scenario 1: Managing Global Supply Chains
A multinational retail giant uses an ERP system like SAP to oversee inventory, logistics, and supplier relationships across continents. This centralized platform ensures that all departments work in sync, avoiding delays and bottlenecks.
Scenario 2: Enhancing Customer Relationships
A mid-sized IT firm leverages Salesforce, a CRM tool, to manage customer data, track sales pipelines, and personalize communication strategies. This approach leads to improved customer retention and higher sales conversions.
Scenario 3: Streamlining HR Processes
An enterprise with thousands of employees uses Workday, an HRMS, to automate payroll, manage benefits, and track performance evaluations, reducing administrative overhead.
Challenges in Enterprise Software Development
While the benefits are significant, enterprise software development comes with its share of challenges:
- High Costs: Developing robust enterprise software requires substantial investment in technology and expertise.
- Complexity: Integrating various systems and ensuring they work seamlessly together is no easy task.
- Change Management: Employees may resist adopting new software, requiring thorough training and a clear change management strategy.
- Data Security: Protecting sensitive business and customer data from cyber threats is an ongoing concern.
Future Trends in Enterprise Software Applications
As technology evolves, so do the possibilities for enterprise software applications. Here are some trends shaping the future:
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI-driven analytics and predictive tools will empower businesses to make smarter, faster decisions.
2. Low-Code and No-Code Platforms
These platforms enable non-developers to create enterprise applications, democratizing the development process.
3. Blockchain for Security
These platforms enable non-developers to create enterprise applications, democratizing the development process.
4. Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
IoT-enabled enterprise software will provide real-time data from connected devices, enhancing operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Enterprise Software Development is the linchpin of modern business operations, enabling organizations to stay competitive, efficient, and customer-focused. From understanding what is enterprise software to exploring enterprise software development services and adopting enterprise software development best practices, businesses can unlock immense value and scalability.
As enterprises continue to embrace digital transformation, investing in robust enterprise applications is no longer optional—it’s essential. Whether you’re looking for tailored solutions, seamless integration, or future-ready tools, the right approach to enterprise software can redefine your organization’s success.
Ready to take the plunge? With the right strategy and technology, the possibilities are endless!
Frequently Asked Questions
- Enterprise software refers to specialized applications or tools designed to meet the needs of large organizations. These software solutions help streamline complex business operations, improve productivity, and enable efficient management of resources, processes, and data. They are scalable, secure, and capable of handling large volumes of users and transactions.
- For instance, it often includes tools for customer relationship management (CRM), enterprise resource planning (ERP), supply chain management (SCM), and human resource management systems (HRMS).
A prominent example is SAP ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning). This software integrates various business functions such as finance, procurement, supply chain, and human resources into a unified system, helping organizations manage their operations efficiently. Other notable examples include:
-
- Salesforce CRM: Manages customer relationships and sales pipelines.
- Oracle NetSuite: A cloud-based ERP solution for financial management and other operations.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365: Offers ERP and CRM solutions tailored for enterprises.
Enterprise systems can be broadly categorized into the following three types:
-
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): Integrates core business processes such as finance, procurement, and production into a centralized system.
-
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Focuses on managing customer interactions, sales, and marketing activities to improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM): Optimizes the flow of goods, services, and information from suppliers to end customers.
These systems often work together to provide a comprehensive solution for enterprise operations.
An example of an enterprise system is SAP ERP. This system provides modules for various business functions, allowing enterprises to manage operations such as finance, logistics, and human resources from a single platform.
-
Other examples include:
-
- Salesforce CRM: A system for managing customer relationships and sales.
- Oracle SCM Cloud: A solution for managing supply chain activities.
- Workday HRMS: A tool for handling human resource functions like payroll and talent management.
These systems are designed to be scalable, robust, and capable of supporting the dynamic needs of large organizations.
Related Program
Recent Blogs
Exciting Opportunities with a Banking and Finance Degree
Top Colleges for MBA in Finance
2 thoughts on “Enterprise Software Development: The Ultimate Guide for Modern Businesses”
-
-
This blog offers valuable insights into enterprise software development, highlighting its importance in streamlining business operations, improving efficiency, and driving growth. A great resource for understanding evolving tech trends in enterprises.
Reply










2 thoughts on “Enterprise Software Development: The Ultimate Guide for Modern Businesses”
Insightful article on enterprise software development! The breakdown of trends and benefits is highly informative. Thanks for sharing this valuable content!
This blog offers valuable insights into enterprise software development, highlighting its importance in streamlining business operations, improving efficiency, and driving growth. A great resource for understanding evolving tech trends in enterprises.