
Unlock Corporate Strategy: Definition, Types, and Real-Life Examples Now
Corporate strategy is the game-changer. It’s the master plan for a business to follow for long-term success, competitive edge, and market leadership. Today, we are going to deconstruct corporate kinds of corporate strategy, understand the different types of corporate strategy, and witness how it has played out through examples of Different types of corporate strategies, and kinds of corporate strategy
It usually deals with important questions such as:
- Which markets shall we compete in?
- How are we going to compete with them?
- Long-term objectives and goals.
- How to manage and allocate the resources effectively?
Corporate strategies typically belong to various classes, each of which prescribes a different way of business growth and value creation.
Table Of Content
What is Corporate Strategy?
Why Corporate Strategy Matters?
Types of Corporate Strategy
Expert Techniques for Corporate Strategy Development
Real-life Examples of Types of Corporate Strategy
Corporate Strategy and the Role of Leadership
How to Determine Whether the Corporate Strategies Are Indeed Successful
Challenges of Corporate Strategy
Future Trends of Corporate Strategy
Programme on Strategic Management by IIM Ahmedabad
Conclusion
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Corporate Strategy?
*Burnie Group
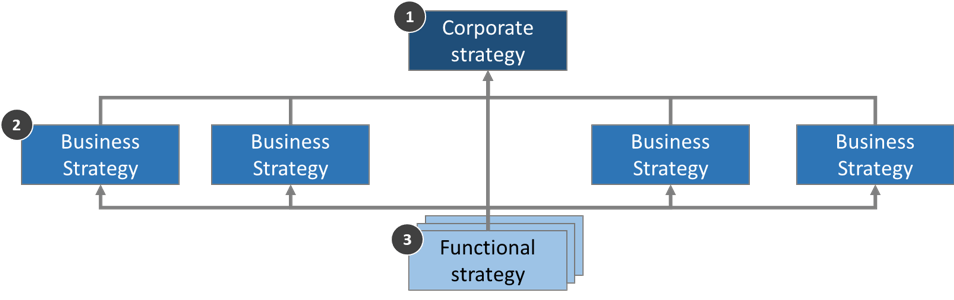
Corporate strategy is the organization’s plan of overall action to achieve long-term goals and objectives. It’s where a company decides how it will compete in the marketplace and what direction it will take to achieve those objectives. IIM Ahmedabad’s Programme on Strategic Management is the most comprehensive course for those wanting to develop a strong understanding kind of corporate strategy and strategic management, thereby preparing to emerge as a leader capable of grappling with the multilayered challenges put forth by the volatile and ever-evolving business environment of the current era.
Why Corporate Strategy Matters?
What are corporate strategies and the different types of corporate strategy so important? Quite simply, because it sets the direction for the whole organization. Without a cogent corporate strategy, business units can drift aimlessly and, in some cases, lose their way, expend resources needlessly, and, now and then, let pass the opportunity for growth. It is what binds different parts of the organization together and ensures that all efforts are made toward meeting the same goals.
Types of Corporate Strategy

The types of corporate strategy are based on every need and are differently shaped and sized according to the different business needs and market conditions. The following section discusses the major types of corporate strategy:
1. Growth Strategy
Growth strategy is one of the types of corporate strategy that tends to focus on an increase in the company’s market share, revenues, and overall size. This objective is achieved through such methods as:
- Market penetration: Increasing sales of existing products in the current markets.
- Market development: Entering new markets with existing products.
- Product development: Introduction of new products to existing markets.
- Diversification: Growth into new products and markets.
Example: Apple Inc. is consistently performing new product development timely by introducing new versions of its iPhones, iPads, and Macs to remain dominant in the market.
2. Stability Strategy
Stability strategies are all concerned about remaining at the status quo. The company opts for these types of corporate strategies when they are doing good, and it thinks there is no reason to shake things up. It involves:
- Maintain Current Operations: Everything is supposed to be left as it is to ensure unproblematic performance.
- Regular Revisions: Make incremental improvements to the product and process.
Example: Coca-Cola almost always adopts a stable corporate strategy by concentrating on its core products and making incremental changes rather than affecting radical ones.
3. Retrenchment Strategy
A retrenchment strategy is a corporate strategy used when a company must downsize to survive or improve its finances. This would mean:
- Divestment: The selling of the underperforming parts of the business.
- Liquidation: Shutting down some segments of the business completely.
- Turnaround: Making major revisions to improve performance.
Example: General Motors used a retrenchment kind of corporate strategy after the financial crisis of 2008 through a reduction of workers, closing down plants, and outsourcing underperforming brands such as Pontiac and Saturn.
4. Corporate Level Strategy
The corporate-level types of corporate strategy look at the overall scope and direction of the entire organization. It defines industries or markets where the company should operate and manages its business portfolio. This comprises:
- Single Business Strategy: A firm focuses on only one primary line of business.
- Diversification Strategy: A firm operates in more than one line of business.
Example: Berkshire Hathaway, under Warren Buffett’s stewardship, holds a corporate-level strategy of diversification. It has investments in insurance, railroads, and consumer goods industries.
5. Corporate Branding Strategy
Corporate branding strategy is the way a company presents itself to the public. It is a company’s most defining feature—the organization’s mission, values, and reputation. The primary ingredients include:
- Brand Identity: Developing a distinctive and personal image for customers that remains consistent.
- Brand Positioning: Setting the brand within the market and against its competitors.
- Brand Equity: Creating value from beliefs concerning a brand held by customers and holding customer loyalty.
Example: The approach of Nike in corporate branding emphasizes innovation, athletic achievement, and creating an emotional bond with the customer. Their “Just Do It” commercial is a living example of a strong brand identity.
Expert Techniques for Corporate Strategy Development
The creation of an effective corporate strategy involves much more than dealing with market trends. It requires the adoption of some analytical tools and frameworks that will guide one through complex decision-making. Some of the key approaches are:
1. SWOT Analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
SWOT is one of the most basic yet most powerful strategic tools. It provides an organization with an insight into not only internal but also external factors that would decide its fate
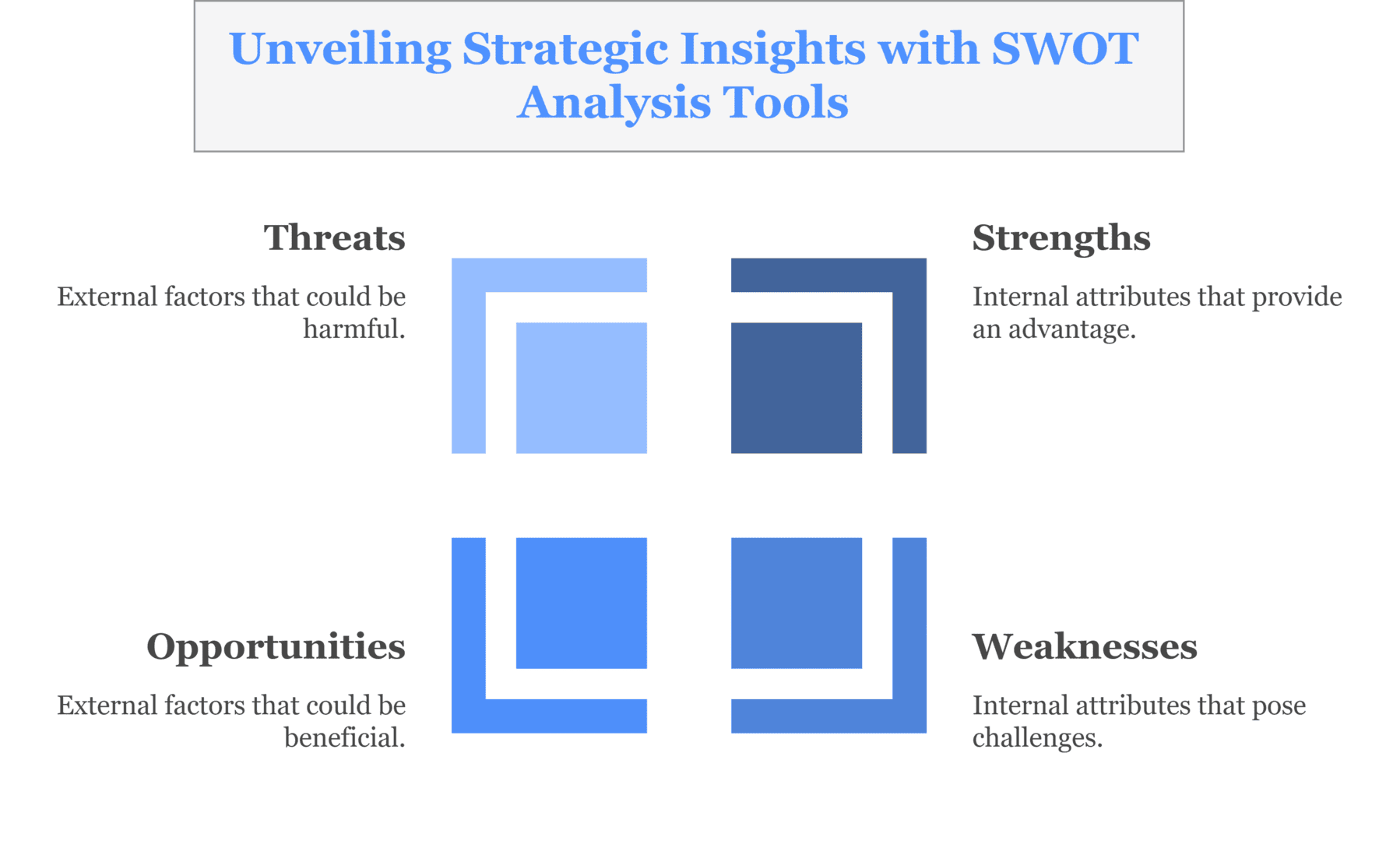
- Strengths and Weaknesses: These are those issues that relate to a firm’s internal structure and operations. In particular, for example, a company’s strong brand or a highly trained workforce can all be considered strengths, whereas old technology or a lack of innovation could be its weaknesses.
- Opportunities and Threats: These refer to external factors. An expanding market or new alliance might spell an opportunity, whereas increased competition or changes in regulations might pose a threat.
2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
The Five Forces framework, developed by Michael Porter, depicts how to calculate the competitive forces of your industry. It includes:
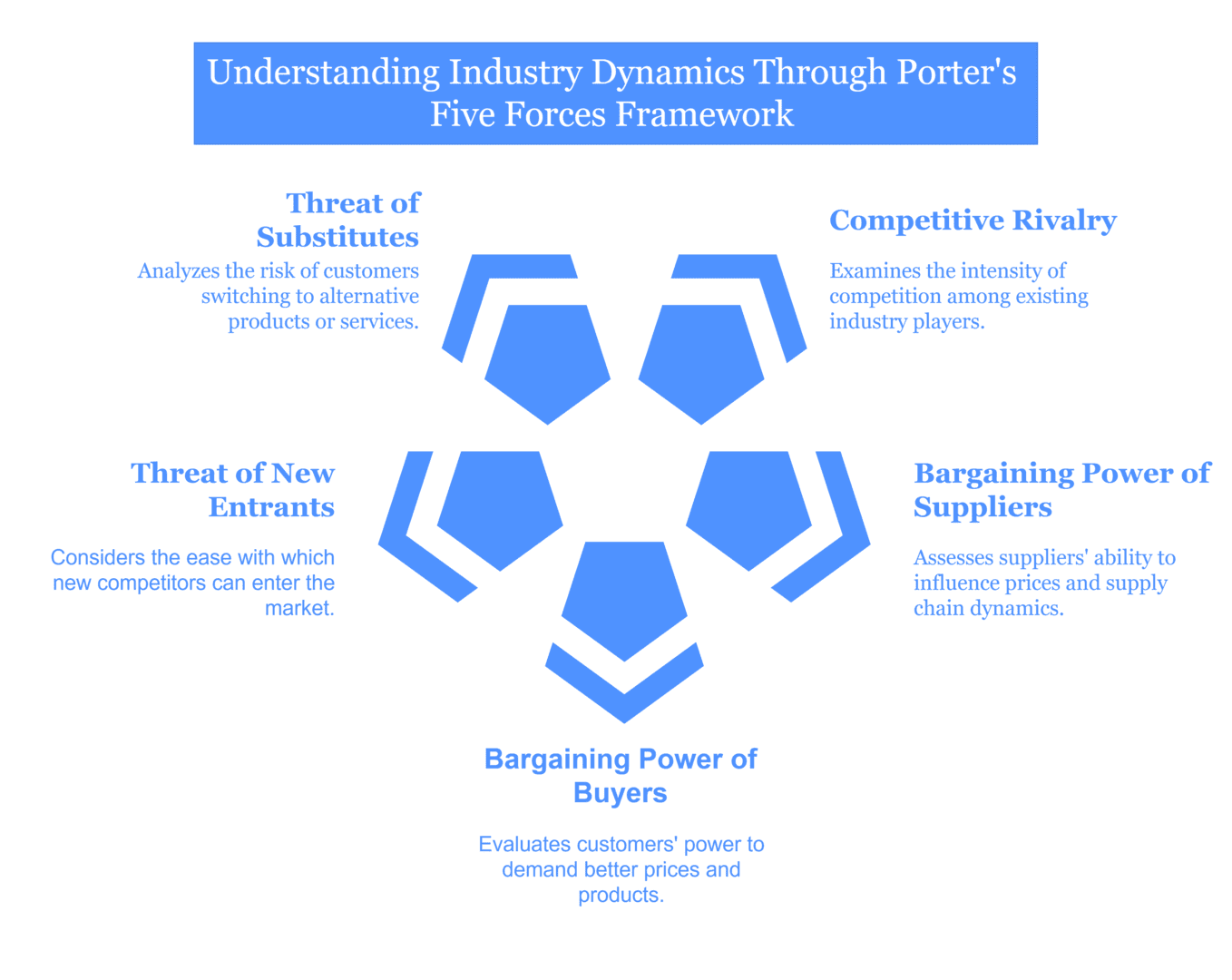
- Competitive Rivalry: How is the rivalry between the existing competitors?
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers: Do suppliers hold high power to affect prices or supply chain logistics?
- Bargaining Power of Buyers: How strong is the influence of customers in demanding lower prices or better products?
- Threat of New Entrants: How easily can new players enter your market?
- Threat of Substitutes: Can customers easily switch to alternatives?
- Why It Matters: This model helps you look beyond the direct competitors and understand other forces that might shape your business environment.
3. BCG Matrix (Boston Consulting Group)
The BCG Matrix is a portfolio management technique that particularly finds its application in large companies dealing with a range of products or business units. The BCG Matrix carves out a company’s products into four categories based on market growth rate and market share.
- Stars: High growth, high market share. These are your top-performing products that need investment to maintain their position.
- Cash Cows: Low growth, high market share. These are established products that provide a steady income with little investment.
- Question Marks: High growth, low market share. These are products with a future but also need cautious decisions on strategy in investing or divesting.
- Dogs: Low growth, low market share. These are normally those products that should be phased out or restructured.
4. Blue Ocean Strategy
The BCG Matrix is a portfolio management technique that particularly finds its application in large companies dealing with a range of products or business units. The BCG Matrix carves out a company’s products into four categories based on market growth rate and market share.
- Example: Companies like Cirque du Soleil didn’t just create a better circus; they redefined the whole concept by integrating theater and circus in a way that no competitor was addressing.
- Why It Works: It allows businesses to step out of the saturated market and find new, profitable spaces.
5. Scenario Planning
As uncertainty is increasing on every front, the relevance of scenario planning is immense. This technique teaches one to envision multiple futures that could occur to help them prepare for any of several eventualities.
- How It Works: You identify the key uncertainties and variables that would affect your business, such as changes in regulations, economic shifts, or the advancement of technology. You then create “what-if” scenarios to see how those variables might play out.
- Why It’s Important: Scenario planning allows you to be flexible, freeing you from the constraints of rigid plans. You’ll be ready to shift or pivot as the future changes course.
6. PESTEL Analysis
PESTEL analysis is a framework that helps companies assess the key external factors (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal) influencing their organization. It provides a comprehensive understanding of the macro-environment in which a business operates.
- Political Factors: These factors include government policies, political stability, trade regulations, tax policies, and any other governmental interventions that can affect the business.
- Economic Factors: Economic factors include economic growth, interest rates, inflation rates, exchange rates, unemployment rates, and the availability of credit. These factors can impact a company’s profitability and growth potential.
- Social Factors: Social factors encompass cultural aspects, demographic trends, population growth rate, age distribution, career attitudes, lifestyle changes, and consumer behavior. These factors can influence consumer demand and preferences.
- Technological Factors: Technological factors include technological advancements, automation, research and development, technological awareness, and the availability of technology. These factors can affect a company’s operations, innovation, and competitiveness.
- Environmental Factors: Environmental factors include ecological and environmental aspects such as climate change, pollution, environmental regulations, recycling procedures, and renewable energy. These factors are becoming increasingly important for companies due to growing environmental concerns.
- Legal Factors: Legal factors include laws and regulations such as employment laws, consumer protection laws, intellectual property rights, health and safety laws, and international trade laws. Companies must adhere to these laws to operate legally and ethically.
7. Value Chain Analysis
Value chain analysis helps identify the activities that create value for a company and its customers. It involves analyzing primary activities (such as operations, marketing, and sales) and support activities (such as infrastructure, human resource management, and technology development) to understand where value is added and where costs can be reduced.
- Primary Activities: These include activities directly involved in producing and delivering a product or service. Examples include inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and service.
- Support Activities: These activities support the primary activities and include infrastructure, human resource management, technology development, and procurement.
- Why It Matters: By analyzing the value chain, companies can identify areas for improvement, reduce costs, and enhance customer value.
8. Core Competency Analysis
Core competency analysis involves identifying the unique strengths and capabilities that give a company a competitive edge. These competencies are typically difficult for competitors to imitate and contribute significantly to customer value.
- Identifying Core Competencies: This involves looking at what a company does exceptionally well, whether it’s in technology, processes, customer service, or innovation.
- Leveraging Core Competencies: Once identified, these competencies should be leveraged to create new products, enter new markets, and enhance existing offerings.
- Why It Matters: Focusing on core competencies allows companies to differentiate themselves and maintain a sustainable competitive advantage.
9. Resource-Based View (RBV)
The Resource-Based View (RBV) suggests that a company’s resources and capabilities are the primary drivers of its competitive advantage. These resources can be tangible (like financial and physical assets) or intangible (like brand reputation, knowledge, and intellectual property).
- Identifying Valuable Resources: This involves assessing which resources are valuable, rare, inimitable, and non-substitutable (VRIN).
- Developing Capabilities: Capabilities are the organizational routines and processes that allow a company to deploy its resources effectively.
- Why It Matters: By focusing on developing and leveraging valuable resources and capabilities, companies can achieve a sustainable competitive advantage.
10. Balanced Scorecard
The Balanced Scorecard is a strategic performance management tool that helps companies translate their strategic objectives into a set of performance measures. It looks at the organization from four perspectives:
- Financial Perspective: How do we look to shareholders?
- Customer Perspective: How do customers see us?
- Internal Process Perspective: What must we excel at?
- Learning and Growth Perspective: How can we continue to improve and create value?
Why It Matters: The Balanced Scorecard helps companies align their activities with their strategic goals, monitor performance, and make necessary adjustments.
In conclusion, the types of corporate strategy and their inherent analytical tools and frameworks are essential for companies to navigate the complexities of the business environment. By understanding and applying these strategies and tools, businesses can effectively plan, compete, and achieve their long-term goals.
Real-life Examples of Types of Corporate Strategy
Let us now elaborate on some examples of the application of corporate strategy in practice with different companies.
1. Growth Strategy at Amazon
Amazon is the prime example of one of the key types of corporate strategy—growth strategy. Starting as an online bookshop, Amazon continued with various products and advanced to the introduction of services like Amazon Prime, later prospecting towards cloud computing with Amazon Web Services. Its unflappable vision for growth helped it dominate quite a few industries.
2. The stability strategy: IBM
IBM, a major global technology firm, uses another key type of corporate strategy—stability strategy. Rather than seeking high growth, IBM seeks market steadiness through steady performance and gradual innovation. Its sustained business over time is due to the emphasis on steady customer relationships and dependability.
3. Tesla’s Corporate Branding Strategy
Tesla’s corporate branding strategy has been based on innovativeness, sustainability, and luxury. The company was able to position itself in the market as a leader in both electric vehicles and clean energy. The identity of the brand includes attributes of leading-edge technology and the environment. This strong brand positioning fostered a loyal customer base and powerful market presence.
4. Diversification Strategy—Disney
Disney is one of the greatest examples of a successful company that applied one of the most unique types of corporate strategy—diversification strategy. With their first product, animated films, Disney entered the theme park, television network, and merchandising industry. Their acquisition of Pixar, Marvel, Lucasfilm, and 21st Century Fox further diversified their portfolio. Today, Disney is considered an entertainment powerhouse.
5. Google’s Corporate-Level Strategy
Google, now Alphabet Inc., demonstrates strong business-level strategies through diversification into different technological arenas. From its core—search engine business—to autonomous vehicles (Waymo), life sciences (Verily), and smart home products (Nest), Alphabet entered each of these businesses with foresight into up-and-coming high-growth areas and was poised to be part of their long-term relevancy and profitability.
Corporate Strategy and the Role of Leadership
The success of all types of corporate strategy lies in the strength of its leadership. The leader of a corporate body should:
| Vision | Adaptability | Decision-Making | Communication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Develop an inspiring and riveting vision for the future. | Based on changing markets, have strategies in place that can be adapted. | Be able to make informed decisions in line with the goals of the company. | The strategy is understood and adopted by the firm as a whole |
Example: The case of Satya Nadella, who took over as the CEO of Microsoft Company and brought the company back on track by re-focusing on cloud computing and AI. This exemplifies the potency of visionary leadership in formulating corporate strategy.
How to Determine Whether the Corporate Strategies Are Indeed Successful
To measure the effectiveness of the types of corporate strategy, some key performance indicators would include:
- Revenue Growth: Improved sales and markets.
- Profit Margins: Enhanced profitability.
- Customer Satisfaction: Level of customer loyalty and engagement.
- Employee Engagement: The morale of employees and improved productivity.
- Market Position: Competitive position and brand strength.
Frequently checking the standalone basis or these metrics would help the companies improve marketing strategies to remain on track to achieve long-term goals.
Challenges of Corporate Strategy
There are indeed several common challenges in the implementation of the various types of corporate strategy. Some of them are:
- Resource Allocation: Make sure the right resources are in place to underpin the plans and can effectively be utilized.
- Resistance to Change: To overcome the internal resistance to the change process and to inculcate a culture that can embrace change.
- Market Dynamics: Keep pace with changes in market conditions due to ever-evolving competitive pressures.
- Execution: Translate the strategic plans into concrete action and focus on getting it done.
Example: The failure of Kodak to adopt the digital photography revolution is a tough lesson learned, with consequences of failing to overcome these challenges. Despite having invented digital photography, Kodak’s reluctance to move from its then-profitable film business led to its decline.
Future Trends of Corporate Strategy
The following are some future trends in shaping corporate strategy types:
- Digital Transformation: The embracing of digital technologies for efficiency and innovations.
- Sustainability: Embedding environmental and social concerns in strategy.
- Globalization: How your company will enter emerging markets and manage your multinational or transnational operations.
- Innovation: Driving a culture of continuous innovation and disruption.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: What big data and analytics mean for your strategy.
Companies that lead in these marketplace trends will be much better prepared to handle future challenges and exploit new opportunities.
Programme on Strategic Management by IIM Ahmedabad
IIM Ahmedabad’s Strategic Management Programme equips leaders to become strategic thinkers—confident in managing a far more complex business landscape. Here’s why this programme is a must for anyone serious about corporate strategy:
- Practical, Actionable Learning: The curriculum isn’t theoretical. Instead, the programme equips you with very real-world tools and frameworks such as SWOT, Porter’s Five Forces, and scenario planning that can be applied at once to your business challenges.
- Expert Faculty: Learn from top-ranked professors who balance academic excellence with hands-on industry experience. They have consulted for companies all over the world, giving you insights that are both deep and pragmatic.
- Digital Transformation: Utilize AI, data analytics, and digital strategy to maintain a competitive edge. Understand how to incorporate digital into your strategy to help you stay ahead in today’s rapidly changing markets.
- Networking & Peer Learning: You’ll learn from and interact with senior leaders across industries, gaining valuable experiences while building a strong professional network that extends well beyond the life of the program.
- Flexible Format: With options for on-campus and hybrid learning, you’ll be able to balance professional life with the latest strategic insight.
Conclusion
The mastering of corporate strategy by the leaders is critical for success in today’s competitive landscape. From a profound understanding of market dynamics to crafting innovative solutions, a good strategy lays the bedrock for long-term success. The IIM Ahmedabad- Programme on Strategic Management equips leaders with advanced tools, frameworks, and real-world case studies that help them craft strategies that drive their organizations forward.
This program, in collaboration with Jaro Education, a leader in online executive education, makes world-class learning more accessible. IIM Ahmedabad has allied with Jaro Education to ensure that working professionals get updated knowledge from one of the premier institutions of India through flexible online and hybrid formats to seamlessly fit into your busy schedule. IIM Ahmedabad combines the best of academic knowledge with the needs of a dynamic business environment through its strong reputation for quality educational experiences.
It enables you to enhance your corporate strategy skills without interfering with your career, blending a rigorous curriculum at IIM Ahmedabad with the comprehensive reach and flexibility of Jaro Education. Be it driving growth in business, fostering innovation, or sharpening your competitive edge, the programme is an opportunity to learn from the best and apply these lessons directly in your leadership journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Apple: Apple is a prime example of successfully using a growth strategy by continuously expanding its product line and entering new markets. It has also used vertical integration to control the manufacturing of many of its components, ensuring quality and reducing dependency on third parties.
- Tesla: Tesla uses a growth strategy by expanding its electric vehicle range and into renewable energy products. It also employs vertical integration by producing its own batteries and software.
- Coca-Cola: Coca-Cola uses a stability strategy by maintaining its dominant position in the soft drink market. It focuses on improving customer loyalty, introducing new flavors, and expanding distribution channels.
The effectiveness of a corporate strategy can be measured using key performance indicators (KPIs) such as:
- Revenue growth
- Profit margins
- Market share
- Customer satisfaction and retention
- Return on investment (ROI)
- Competitive positioning
Regularly assessing these KPIs allows companies to determine if they are on track to meet their long-term goals and make necessary adjustments to their strategy.

