
Information security and cyber security are frequently used together as both take the responsibility for maintaining the safety of computers and protect them from dangers and data breaches. When we discuss data security, protecting the data from attacks by malicious users is the main focus. The fact that “not all data can be information” is a vital issue, but data can still be informed if it is understood for its context and given meaning.
Cyber threats and offences are becoming more frequent. To properly address these urgent issues, more people should enter this field. If you are interested in accelerating your career in the field of cybersecurity, you must enrol in IIM Indore‘s Executive Programme in Cyber Security for Organisations. The purpose of this cyber security course is to provide learners with a thorough understanding of cybersecurity. Numerous subjects are covered in the course material, such as threat analysis, managing risks, network safety, and safety policies and strategies.
Definition of Cyber Security
Cyber security is the capacity to secure, defend and protect electronic data from attacks and exploitation in servers, mobile devices, computers, networks, and other devices. For preserving this data, it is important to identify the risks to which the data is exposed and the location of the data. It protects critical and sensitive information against threats and unauthorised intrusions.
Definition of Information Security
It is a form of data security which is also known as infosec and refers to data protection using various forms and strategies. It provides access to data to only a few authorised people, unlike cyber security, which involves security from cybercrime. As a professional in this field, one must maintain the data’s confidentiality, integrity, and availability (CIA). Today, most data is stored in electronic devices such as computers, servers, or in cloud storage.
Essential Differences between Cyber Security and Information Security
Table of Contents
Data protection from unauthorised access and malicious activity is the main aim in the fields of information security and cyber security, which are closely related. People often confuse the two terms, but they have distinct differences.
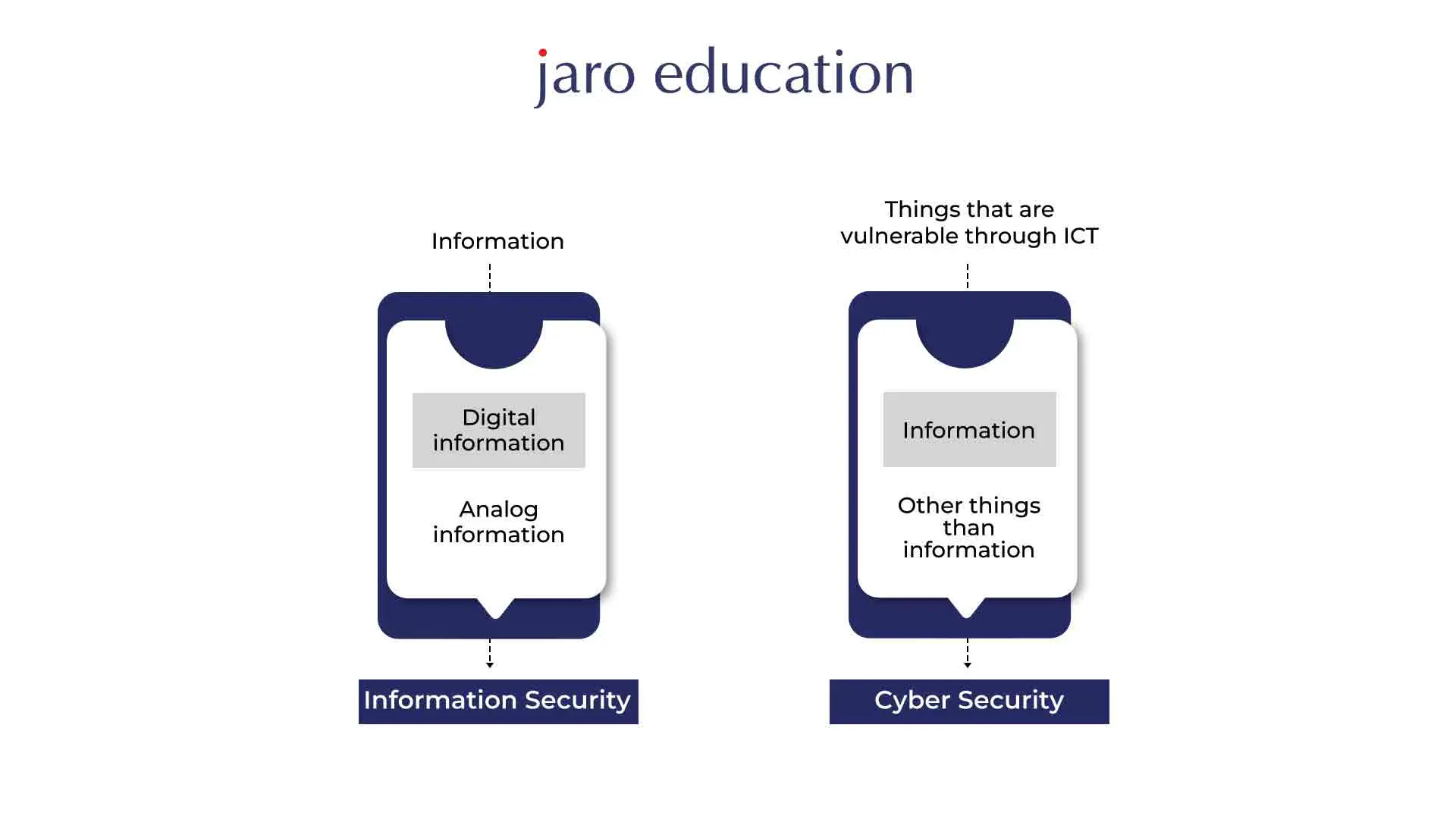
Information Security focuses on safeguarding all forms of data, regardless of its location or format. This includes electronic files, physical documents and any other information that holds important value for an organisation. The main work of Information Security personnel is to give assurance for the security, privacy, and accessibility of data by implementing appropriate measures such as access controls, encryption, backups, and disaster control plans. Information Security professionals prioritise understanding the data sources and assessing potential risks before addressing specific threats.
On the contrary, Cyber Security primarily protects digital data in cyberspace from external threats. Its main objective is to protect data that is stored, processed, or moved across computer systems and the internet. Protecting against viruses, malware, trojans, attackers, and other dangerous actions that can endanger the privacy, reliability, and accessibility of digital data is the responsibility of cyber security experts. They use technologies like intrusion detection systems, firewalls, antivirus programmes, and safe network setups to deal with advanced and complex threats.
While information security covers a broader scope, including physical and non-digital data, cyber security specifically concentrates on securing data in online platforms. Information security professionals often lay the foundation for overall data protection by implementing measures to secure data sources, whereas cybersecurity experts focus on combating cyber threats that specifically target digital information.
*Cisoplatform
Similarities between Cyber Security and Information Security
Information security and cybersecurity overlap in several ways, including shared security practices and similar educational requirements and skill sets.
One of the critical areas of overlap is using the CIA triad model to develop security policies. Both information security and cybersecurity professionals want to preserve the confidentiality of data by limiting access to authorised individuals and protecting it from any kind of unauthorised disclosure. They also focus on maintaining the originality of information, ensuring it is accurate, not altered, and reliable.
In the field of education and skills, information security and cybersecurity careers often require a bachelor’s degree in cybersecurity, IT, computer science, or any related disciplines. These degree programs provide a foundational understanding of security principles, technologies, and practices. Professionals in both fields also benefit from being familiar with several technologies, including database user interface and query software, virus-protecting tools, network monitoring software, and web platform development. Information security and cybersecurity professionals need to have strong analytical and problem-solving abilities and a clear understanding of computer systems and networks. They should be knowledgeable about security protocols, encryption techniques, and risk assessment methodologies. Effective communication and teamwork skills are also essential, as they often collaborate with colleagues and stakeholders to address security issues.
While information security and cybersecurity have distinct focuses and areas of expertise, they share standard security practices and require similar educational backgrounds and skill sets. This similarity allows professionals in these fields to collaborate together to protect data and reduce or avoid risks.
Job Profiles for Cyber Security and Information Security
Careers options for both information security and cybersecurity are addressed in this section.
Information Security
Information Security Analyst
The individuals in this position are responsible for planning, monitoring, and implementing security measures to protect computer networks and information. They may also create reports on security metrics and data breaches.
Information Security Specialist
Similar to analysts, information security specialists work on developing and implementing information risk management frameworks, standards, and policies. They assist users in accessing databases and participate in risk assessments.
IT Security Consultant
IT security consultants assess and recommend improvements to an organisation’s information security. They support data privacy improvements, identity access management systems, cybersecurity management and operations.
Cyber Security
Cybersecurity Analyst
The analysts focus on protecting data from cyberattacks. They detect threats and incidents and respond to data breaches. They may also develop cybersecurity awareness training and conduct forensic analysis.
Cybersecurity Engineer
These professionals oversee the development of cybersecurity procedures and policies. They build and maintain firewalls, develop security controls for digital files, and monitor and respond to security breaches.
Penetration Tester
Penetration testers identify vulnerabilities in systems by conducting simulated cyberattacks. They exploit systems and gain access to sensitive information to suggest security solutions and improvements for better defences against malicious attacks.
Salary ranges for these roles can vary depending on experience, location, and industry demand.
Types of Cyber Security Measures
Professionals have to deal with different types of cyber security regularly. Some of them are:
1. Network Security
This protects computer networks from misuse, unauthorised access, interruptions, and service disruptions. It involves implementing firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and virtual private networks (VPNs) to protect network infrastructure.
2. Cloud Security
It has a set of procedures, controls, technologies, and policies that work together to keep cloud-based systems and infrastructure secure. It involves measures to protect data stored in the cloud, secure cloud-based applications, and ensure the privacy and compliance of cloud environments.
3. Application Security
Application security involves processes to detect, fix, and enhance the security of applications. It aims to prevent hackers from exploiting application vulnerabilities to gain unauthorised access or steal sensitive data. Application security measures include code reviews, vulnerability assessments, and penetration testing.
4. Critical Infrastructure Security
It focuses on protecting essential systems and services that are vital for the functioning of society, transportation systems, and network communication. It involves implementing security measures to safeguard critical infrastructure from cyber threats, which can have severe consequences if compromised.
These are just a few examples of the types of cyber security professionals work with. Each type of cyber security addresses specific threats and requires specialised knowledge and tools to protect against them effectively.
Types of Information Security Measures
There are different types of Information Security measures organisations employ to protect their data:
1. Access Controls
It determines who can access the organisation’s network and data. They involve restricting physical and virtual access to the company’s infrastructure. To ensure that only people with the proper authorisation can access sensitive information, this includes authentication of users, approval, and other procedures.
2. Compliance Controls
Compliance controls focus on maintaining cybersecurity standards and privacy laws. They enforce requirements for data security and often involve conducting risk assessments, implementing data protection measures, and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations.
3. Procedural Controls
It helps to detect and reduce security risks to physical assets and overall organisational security. They involve establishing procedures and guidelines for security practices, conducting security awareness training for employees, implementing incident response plans, and establishing a security framework to manage and mitigate security risks.
4. Technical Controls
Technical controls cover different technological measures to enhance security. This includes implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) for login, using antivirus software and firewalls to protect against malware and unauthorised access, encrypting data, and employing intrusion detection and prevention systems. These controls add an extra layer of security to protect the organisation’s data and systems.
Conclusion
The two types of data security are vital for the security of organisational data. Learning about the criticalities of these two segments requires proper guidance and resource. You must participate in a training programme in this field if you want to work as a certified cyber security professional in a reputable company earning a high salary.
To master the art of cybersecurity, the Executive Programme in Cyber Security for Organisations at IIM Indore can be your suitable option. Join this programme through Jaro Education to receive valuable training from professionals, gain useful knowledge, and engage in beneficial discussions.








