What Are Footprinting and Reconnaissance?
Table of Contents

- jaro education
- 18, July 2023
- 3:00 pm
Understanding the methods used by malicious individuals in the wide and constantly changing field of cybersecurity is essential for safeguarding sensitive data and preventing unauthorised access.
Footprinting and reconnaissance are the two core tasks that each cyber attack is built upon. In order to find weaknesses and potential entry points, these pre-attack procedures entail acquiring data about a target system or network. Organisations may improve their defensive tactics and strengthen their cybersecurity posture by comprehensively understanding of the theories and techniques behind reconnaissance and footprinting.
This page seeks to give a general overview of footprinting and reconnaissance, illuminating their terms, objectives, methods, and more.
Furthermore, with the increasing need for cybersecurity professionals, it is vital for individuals to acquire the necessary knowledge and skills to combat these threats effectively. One program that can help students in this domain is the Executive Programme in Cyber Security for Organizations [EPCSO] offered by IIM Indore. This programme aims to train individuals in understanding, preventing, and responding to cyber threats effectively.
What is Footprinting?
Footprinting is the process of identifying and understanding the security risks in an organisation. It involves gathering information about the target, both from publicly available sources and through more intrusive methods. This information helps build a profile of the organisation’s security posture and identify vulnerabilities. The approach used depends on the desired information and level of access.
What is Reconnaissance?
An important step in ethical hacking is reconnaissance, which includes leaving digital footprints. Data on the target system’s network infrastructure, personnel information, and security rules are collected as part of this process. Finding potential attack routes and vulnerabilities is the aim of reconnaissance. Security policies, network specifics, employee contacts, and host information for vulnerability assessment are all pieces of information that are gathered while accomplishing this step.
Types of Footprinting
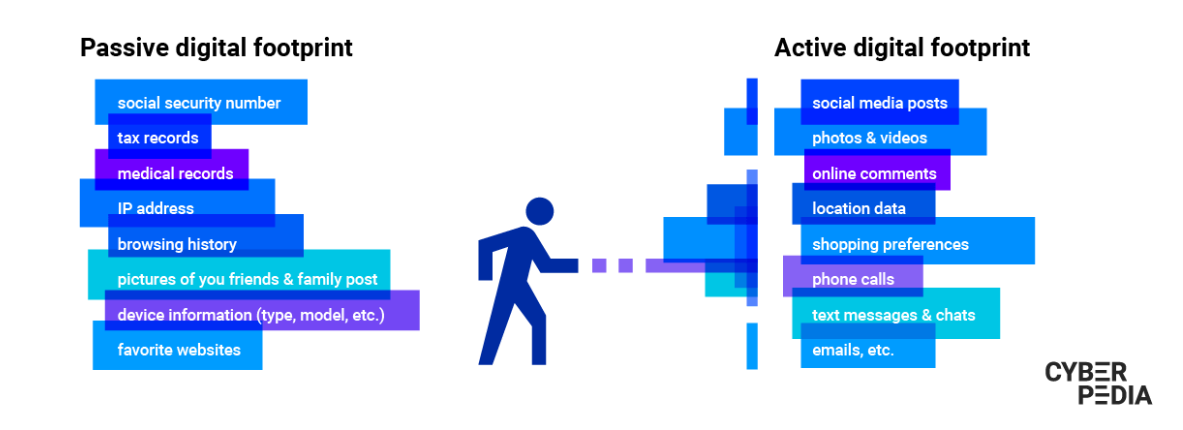
There are two types of footprinting. Active methods may include hacking or social engineering, while passive methods focus on publicly available data. Both types are based on how information is gathered:
Passive Footprinting
In this type of footprinting, the attacker collects information about the target without directly interacting. It is useful for gathering undetected information. The attacker utilises publicly accessible data from online sources and analyses the target organisation’s website. Valuable information can be obtained about customers, employees, history, and more.
Passive footprinting methods offer additional options, including:
Browsing the target's website
Exploring the website to gather insights and potential vulnerabilities.
Target monitoring using alert services
Using monitoring tools to receive updates on changes or activities related to the target.
Examining an employee's social media accounts
Extracting information from publicly available profiles of individuals associated with the target.
Obtaining location information using web services
Obtaining geographical information about the target through various online services.
Finding the website using WHOIS
Acquiring domain registration and contact information.
Using search engines
Conducting targeted searches to gather information about the target.
Social networking site social engineering
Employing manipulation techniques to extract information from individuals on social media platforms.
Obtaining information about infrastructure from employment sites
Collecting information about the target’s infrastructure through job postings or descriptions.
Financial services used to obtain monetary information
Extracting relevant financial data about the target organisation.
Active Footprinting
In active footprinting, the attacker directly interacts with the target to gather information. This approach increases the likelihood of the target detecting the activity. Methods used in active footprinting include human interaction, searching for digital files, email tracking, social engineering, performing WHOIS lookups, traceroutes, and more.
Active footprinting techniques can be applied in various ways, such as:
Traceroute analysis
Tracing the network path to identify routers and potential vulnerabilities.
Email tracking
Gathering information by tracking email interactions and analysing metadata.
Whois lookup
Retrieving domain registration information to gather details about the target.
Extracting DNS information
Gathering data related to the target’s domain names and associated IP addresses.
Methodology of Footprinting
Footprinting follows a systematic approach consisting of four main steps:
Assess goals
Before starting the footprinting process, it is crucial to define the objectives or goals of the assessment. This helps in focusing efforts and determining the purpose of the information to be gathered.
Gather information
Once the goals are established, the next step is to collect relevant information about the target. This includes obtaining details such as the company’s name, website, contact information, and any publicly available information on social media platforms. It also involves investigating the target’s security measures and infrastructure to gain insights into potential vulnerabilities.
Analyse information
After gathering the necessary data, it needs to be analysed and evaluated. This involves assessing the potential threats and weaknesses that the collected information reveals. By identifying vulnerabilities and potential attack vectors, it becomes possible to understand the target’s security posture and the risks it faces.
Report findings
The final step is to document and report the findings of the footprinting process. A detailed report is created, outlining the conclusions drawn from the analysis and providing recommendations to enhance the target’s security posture. This report serves as a valuable resource for the target organisation, enabling them to be aware of cybersecurity threats and take appropriate measures to mitigate risks.
Collected Data from Footprinting
There are several uses for the data gathered during a footprinting evaluation. It helps to improve an organisation’s security by identifying weaknesses and recommending remedial actions. Additionally, the data is useful for assessing security efficacy during later penetration tests. Finally, it serves as proof of the company’s proactive security efforts in the case of a data leak or hack.
Footprinting uncovers cybersecurity vulnerabilities and provides valuable information. Hackers also employ footprinting to gather target details for planning attacks, including employee names and contact information.
Tips to Prevent Footprinting
By following the given preventive measures, organisations can reduce the risk of footprinting and enhance their overall security posture.
Limit information exposure
PMinimise the amount of sensitive information publicly available, such as employee names, contact details, and infrastructure details.
Secure DNS records
Ensure that DNS records are properly configured and not easily retrievable from public servers, reducing the potential for attackers to gather information.
Implement access controls
Apply strict access controls to restrict unauthorised individuals from accessing sensitive data or systems.
Employee training
Educate employees about the risks of social engineering and the importance of safeguarding sensitive information.
Regular vulnerability assessments
Conduct regular assessments to identify and address potential security vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them.
Monitor online presence
Monitor online platforms, such as social media, to identify and address any unintended information leakage.
Stay updated with security patches
Regularly update and patch software and systems to protect against known vulnerabilities.
Network segmentation
Implement network segmentation to compartmentalise sensitive data and restrict unauthorised access.
Incident response plan
Develop an incident response plan to address potential security breaches promptly and effectively.
Final Thoughts
Footprinting and reconnaissance play a crucial role in understanding an organisation’s security posture and identifying potential vulnerabilities. Footprinting involves gathering information about a target system, while reconnaissance is the broader process of information gathering in ethical hacking. By conducting thorough reconnaissance footprinting, security professionals can assess risks, strengthen defences, and prevent potential cyber threats.
To further enhance knowledge and skills in the field of cybersecurity, the Executive Cyber Security course IIM Indore through Jaro Education is an excellent opportunity for cybersecurity professionals. This program provides a comprehensive curriculum that covers various aspects of cybersecurity, including footprinting and reconnaissance techniques. By enrolling in EPCSO, students can gain valuable insights, practical experience, and industry-relevant expertise to effectively address cybersecurity challenges and protect organisations from emerging threats.












3 thoughts on “What Are Footprinting and Reconnaissance?”
Great explanation of footprinting and reconnaissance! Your clear breakdown of these essential cybersecurity concepts is informative and easy to understand.
Your kind words are much appreciated! We are glad you found the content valuable and interesting. You can access more such informative blogs on our website.
Thank you for your generous comment! It’s great to hear that the post was valuable to you.