
- jaro education
- 25, April 2024
- 10:00 am
Businesses use various tools and models to make crucial decisions on mergers and acquisitions, launching a new product, delving into a new product category, and evaluating the financial position to gauge potential risks. Financial modelling is one tool corporations use to assess an investment opportunity and associated risks, forecast financial performance and compare their company’s valuation with competitors.
In financial modelling, all expenses and income of the organisation are recorded in a spreadsheet, and decision-makers use this information for various analyses. Read along to learn more about financial modelling and delve deeper into its various dimensions.
What is Financial Modelling?
Financial modelling is forecasting a company’s or any project’s economic performance by analysing financial metrics like income and expenses, growth and risk factors. In the corporate world, financial modelling is one of the most important tools as the analysis can give a fair idea regarding the prospects of a project or investment in the coming years. It will help determine the return on investment and cash flows the project will generate in the next 5-10 years.
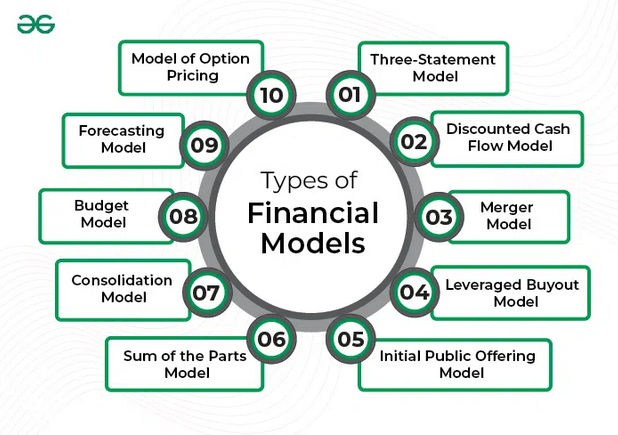
One of the biggest reasons why organisations prefer to go for financial modelling is its flexibility. Financial modelling allows working and interacting with individual units without tinkering with the entire structure. It is helpful for volatile inputs as there is scope for changing inputs without affecting the model as a whole.
Now that you have understood the meaning of financial modelling let’s shift our focus to other aspects of this concept.
Table of Contents
Role of Financial Modelling in Corporate Decision-Making
Financial modelling plays a crucial role in the decision-making process related to any investment and the business’ financial analysis. The results given by financial modelling help corporations conduct a fair and objective evaluation of their organisation. Notably, financial modelling plays an essential role in the following decision-making process:
- Mergers and acquisitions
- Raising capital
- Whether to enter any market
- Open a new office or store
- Divesting business assets
- Management accounting
- Finding out the company’s valuation
- Analysis of financial statements
- Budgeting process
Strategic Planning and Forecasting
In this section, we will discuss strategic planning and forecasting and how the financial modelling process accelerates a business’ planning and forecasting functions. There are three ways in which financial modelling helps the company in the process of strategic planning, and these are discussed below:
- Scenario Analysis: Financial modelling allows companies to make nuanced decisions through scenario simulation and assess the efficacy of different strategies in different scenarios. A proper scenario analysis will help the company make informed choices that align with the organisation’s objectives.
- Resource Allocation: Resource allocation is linked to forecasting, that is, how well companies can see future trends and adopt suitable strategies accordingly. Financial modelling is critical in efficient resource allocation and identifying inefficient, unproductive, and wasteful expenditures. Furthermore, with the help of financial modelling, companies can locate high-growth future opportunities and allocate resources in such a manner that they add maximum value.
- Setting Realistic Targets: Another solid usage of financial modelling in planning is setting realistic goals. Financial modelling is a data-driven process and allows companies to establish ambitious yet realistic goals. Organisations compare their competitors’ positions in the market and set goals accordingly.
Capital Budgeting and Investment Analysis
Both capital budgeting and investment analysis are a significant component of financial modelling. Capital budgeting is a process that occurs as a part of investment analysis. Capital budgeting is a process that evaluates the inflow and outflow from a particular business and gauges its profitability. If inflows exceed outflows, then the project is profitable, and companies advance.
Capital budgeting will be successful if the company has completed thorough market research and has an idea regarding overall market conditions. There are several stages in capital budgeting, which are discussed in chronological order as follows:
- Opportunity identification
- Investment proposal
- Data collection
- Deciding the method of evaluation
- Cash flow prediction
- Risk assessment
- Comparison with competitors
- Decision-making
- Performance review
Risk Management and Sensitivity Analysis
Every project comes with several potential risks. Understanding complete project management can be quite challenging due to the complexities involved and the involvement of many factors that can alter a project’s outcome. To overcome these challenges, sensitivity analysis comes to the fore as it acts as an early warning system for companies. The main objective of sensitivity analysis is to assess the risk factors in any specific project or investment. In other words, sensitivity analysis tells companies about all the factors and issues that have or will prevent them from achieving their desired objectives.
The sensitivity analysis process ranks all risks and threats from highest to lowest. The next step is for the companies to formulate strategies to overcome or mitigate these risks. A proper financial modelling system serves as the base on which a company can execute a sensitivity analysis of risks involved in a project.
Financial Reporting and Analysis
Financial reporting and analysis is a popular method of financial modelling. It is the process in which the company analyses and tracks its financial data monthly, quarterly and annually. Entrepreneurs use the output from this process to make strategic decisions, attract new investors, and comply with government regulations. With the rise of AI and machine learning, several financial reporting and analysis software are available to automate tasks like data collection, entry, and structuring.
Here are some of the most common ways of financial reporting:
- Income Statement: It allows for analysis of the income and expenditure of a company. This is the most basic financial reporting system, determining whether a company is profitable.
- Balance Sheet: This has all the information about assets, liabilities and equities held by different stakeholders in the company. A balance sheet financial analysis informs corporations about the company’s current financial health.
- Cash Flow Statement: This statement records all the cash inflows and outflows over a particular period, such as monthly, quarterly or annually. The cash flow statement contains several components of the balance sheet and income statement and is quite potent for efficient business management.
Now, let’s discuss the uses of financial reporting:
- Internal and external decision-making
- Transparency in business functioning
- To raise capital
- Management of financial ratio
Key Components of Financial Models
A financial model utilises several formulas and related assumptions and links these to the different components of economic models to get an idea regarding the company’s future growth. Four critical elements of financial modelling help build a structure and provide a methodology for financial analysis. They are as follows:
- Income Statement: As the name suggests, it records all the revenues and expenses incurred by the company quarterly or annually. A simple income statement analysis will tell decision-makers whether the company is profitable or not. Companies can then make systematic adjustments in their vision and methods to arrest the losses or increase profits, as the case may be.
- Debt Schedule: This tells the amount of debt standing in the company’s name in the form of loans, bonds and debentures. The debt schedule will offer insights into the total interest and principal payments the company must make yearly and leverage ratio analysis.
- Cash Flow Statement: It records the company’s cash generated and payments made towards expenses. It is one of the most essential components of financial modelling as it tells how the company is engaged in its operating, financing and investing activities.
- Balance Sheet: It is the most fundamental component of financial modelling and helps determine the company’s financial health. A balance sheet records all assets, liabilities, capital and shareholder’s equity ratio.
Data Inputs and Assumptions
Data inputs and financial assumptions are critical variables in the economic modelling process. These are pretty useful in forecasting the company’s performance and growth. This happens because the prediction or forecast occurs after considering the data and various financial assumptions. Simply put, the assumption of financial modelling is about predicting the company’s future growth after analysing past datasets from balance sheets, income, and cash flow statements.
One thing that business leaders need to consider carefully is the fact that all the financial modelling assumptions are based on data. Hence, particular emphasis should be placed on collecting and structuring datasets in a composite and error-free form.
Formulas and Calculations
This section will deal with all the major formulas and calculations in the financial modelling processes:
- NPV or Net Present Value: It helps determine a company’s profitability. The net present value model is an ideal choice for analysing a project’s feasibility as it considers the time value of money.
Net Present Value = Current Cash Inflows – Current Cash Outflows
- IRR or Internal Rate of Return: This is also used to assess the profitability of a project. As the name suggests, IRR focuses only on internal factors like the inherent cash flows arising from a project and excludes any external factors like inflation or cost of capital.
IRR = (Cash Flows)/(1+r)^i – Initial Investment
In this formula, r stands for discount rate and i stands for the time period.
- PMT: It is a widely used utility in financial modelling. It tells about the payments made against loan repayment in interest and principal. The wholesome approach followed by the PMT system allows analysts and decision-makers to understand the company’s financial health and the capacity to repay all financial obligations.
Scenario Analysis and Sensitivity Table
The sensitivity analysis of every business scenario is a critical aspect of financial modelling. It enables an understanding of any risk or uncertainties in the output presented by financial modelling due to changes in the input. The analyst will create different scenarios like GDP changes, government policy shifts, and inflation rates and then test the robustness of output presented by financial modelling.
Output and Visualisation
Let’s see the significance of analysing the output given by the financial modelling process. It is vital to have a wholesome perspective of the model’s output and not look at it in isolation. Sometimes, the output offered by financial modelling can be misleading and tempt board members to make wrong decisions. Therefore, board members should rely on more than just the output provided by the financial models and cross-check the final output with other metrics and variables.
Furthermore, a proper discussion on the output with every stakeholder is necessary to get impartial, diverse viewpoints. The process of output analysis is very critical as all strategies and future objectives will be formulated based on what the board members interpret from the output of a financial model.
Best Practices in Financial Modelling
Some of the best practices in financial modelling are discussed below:
- Objective: The financial model should always have a concrete objective to achieve. Hence, it is essential to identify and clearly define such targets. Apart from this, you must identify data sources, key stakeholders, and financial assumptions that will play a critical role in financial modelling.
- Standardised Templates: These ensure consistency and accuracy in data collection, segregation, and analysis. Templates can be customised as per your objectives, but fundamental concepts should not be eliminated.
- Data Validation: Data collected from different sources should be cross-checked and authenticated to eliminate duplication and error in datasets. A separate team consisting of specialists for data validation will be beneficial as the volume of data can be very high and technical.
- Assumptions: The next thing is to take care of the assumptions and ensure they are consistent with past trends. While determining assumptions, you can also conduct a sensitivity test to understand changes occurring in output.
- Formulas: Using proper formulas and statistical tools is vital, as the entire output is based on your formula. Check the formula twice before using it, and ensure you put the correct data in all variables.
Validation: This entails comparing the output with the actual results. If there is a divergence between the two, conduct a thorough analysis of the financial modelling system and fix the errors and biases.
Ensuring the Accuracy and Reliability of Data Inputs
Data accuracy and reliability are non-negotiable concepts, and every organisation undertaking financial modelling should follow some steps to ensure that data is error-free and impartial.
- Have a Clearly Defined System for Data Entry: The employees and department working on data handling should be given clear instructions about following guidelines and standardised templates while carrying out their activities.
- Imbibe the Significance of Accurate Data: During the training programme, employees should be given special emphasis to understand the importance of accurate data and the consequences of error-laden data entry.
- Identify the Core Reason behind Inaccuracy: Data collection and structuring can involve many people and scenarios. Therefore, there can be several factors behind inaccurate data collection and entry. Identify all these internal and external factors and take steps to address each of them individually.
- Efficient Use of Technology: Reducing human interface in non-core areas can significantly increase data reliability. Technology can be expensive, but the benefits far outweigh the costs, so there should be more use of technology to improve data accuracy.
Building Flexible and Scalable Models to Accommodate Changes
Every financial model which offers output for strategic decision-making should be flexible and easily scalable so that changes can be easily made in the system. A flexible financial model will allow changes in assumptions, data input and different scenarios through minimum time and effort. One of the significant benefits of such a system is that it gives space to make amendments for errors in data inputs and analysis.
A flexible financial model will save the company time and money. Any new information can be incorporated into the existing model without altering the core component. It will lead to quick decision-making as companies do not have to change the entire system for changes occurring in one input.
Documenting Assumptions and Methodologies for Transparency
Documentation of methodologies and assumptions fosters transparency and credibility. Documenting all the methods and assumptions in the financial modelling process will reduce arbitrariness and improve stakeholder coordination. Here are some of the tips that you can follow for documenting assumptions and methodologies used in financial modelling:
- Have a Standard Format: The first thing is to have a standard format for storing and structuring data, which is easy to keep track of and understand for all participants. A standardised template will lead to better organisation, fewer mistakes and better coordination.
- Categorise Assumptions: Categorising assumptions as per their relevance and influence is another thing that needs to be followed while documenting. Suppose you can categorise assumptions into facts, estimates, or wild guesses. All these will ensure a more critical evaluation of the financial model and result in better analysis.
- Explanation of Logic: Another reason documentation of assumptions and methodologies is necessary is that it can better explain the logic behind adopting a particular assumption. It enhances transparency and also allows decision-makers to justify their choices.
- Review Assumptions: Another thing that documentation of assumptions and methodologies helps is the ability to review and update them frequently. If assumptions are documented, then you can review and change assumptions as the situation demands. It enhances the flexibility quotient of financial modelling.
Validating and Testing Models for Accuracy and Robustness
The significance of testing financial models has been discussed below:
- Firm Decision-Making: A validated financial model will lead to better decision-making. Board members have more confidence in the validated model output than in non-validated ones. They make wise decisions regarding risk mitigation strategies and resource allocation.
- Mitigation of Risk: A financial model helps forecast business performance. Proper validation and testing of the model will ensure early identification of uncertainties and future challenges.
- Increased Trust: A validated financial model increases trust and credibility amongst board members, investors, shareholders and regulatory agencies. All these stakeholders will be able to make more authenticated decisions.
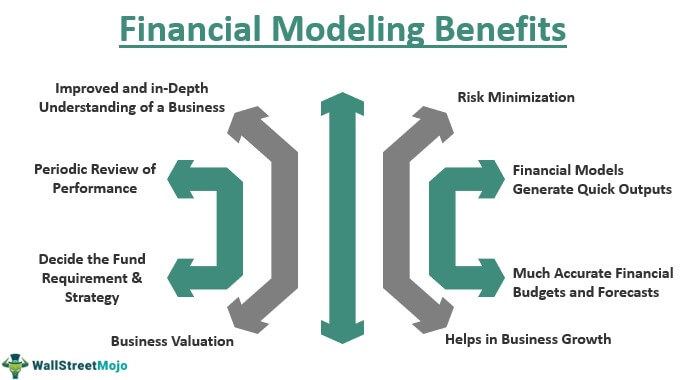
Impact of Financial Modelling on Corporate Decision-Making
Let’s discuss the major benefits of using financial modelling in corporate decision-making:
- In-depth Business Understanding: A well-functioning financial model can be developed only after understanding all the nitty-gritty of the business. The analyst has to grasp a complete understanding of business operations and different factors which can influence its trajectory. Business leaders who develop a financial model understand their business more than their competitors who do not carry out this exercise.
- Performance Review: A variance analysis gives a fair idea about the financial performance of a business. The economic modelling will help execute the variance analysis by comparing budgeted expectations with actual results. With the help of financial modelling, companies can undertake periodic reviews of their functioning.
- Business Valuation: Another impact of financial modelling on corporate decision-making is the importance of determining a business’ valuation. Free cash flows generated by the company will give an idea about the valuation, and the only way to find free cash flows is through financial modelling.
How Financial Modelling Influences Strategic Decisions: Examples
Let’s consider an example of how financial modelling influences the strategic decision-making of a company:
Take an example of a merger and the impact of financial modelling in assessing whether the merger is feasible. In simple terms, a merger refers to two companies becoming a single entity. There is one small company (X Pvt Limited) and one large company (Y Private Limited). The small company is merging with the large company. Let’s see whether the earnings per share of Y Private Limited increase or remain the same post-merger. Apart from this, financial modelling will also determine whether the overall valuation of Y Pvt Limited will increase after the merger.
It is vital to consider both companies’ cash flow and income statements in this case. Other variables include the cost of the merger, payment mode (cash, bonds or equity shares) and the synergies. The Board of Directors of Y Pvt Limited will consider the output from financial modelling to decide whether to proceed with the merger.
Case Studies Highlighting Successful Applications of Financial Modelling in Real-world Scenarios
Several companies have successfully used financial modelling to carry out many activities like mergers and acquisitions, assessment of the feasibility of new investments and projects, raising capital, and capital budgeting. A discounted cash flow model is the most popular financial model in investment banking and capital market research.
Challenges of Financial Modelling in Decision-making Process
The major challenges of adopting financial modelling in corporate decision-making are as follows:
- Time Consuming: One of the biggest challenges of financial modelling is its time-consuming process. A financial model consists of several stages, with complex tasks at each stage. It costs the company a lot of resources and time and is not feasible for small companies.
- Inaccurate: There have been many instances worldwide where financial modelling has proven incorrect. One of the major examples of its failure is the 2008 subprime lending crisis. Predicting different variables, like interest rates, taxation policies, consumer trends, etc., is complicated. As a business, you would be doomed if you solely rely on financial modelling while making crucial decisions.
- Non-consideration of Soft Factors: A business is not only about numbers and statements. Soft factors like synergies, consumer loyalty, and company culture are important but should be considered when doing financial modelling.
Conclusion
Financial modelling is a vital tool that organisations adopt when they forecast their performance, make mergers and acquisition deals, assess the financial feasibility of a project, etc. However, business leaders should also consider other financial management tools before making any decision.
If you want to be a financial modeller and wish to study what is financial modelling, how it functions, and its various components and benefits in-depth, then it is important to get admission to a reputable course.
Wish to know more? Connect with Jaro Education and check out certified courses related to financial modelling, such as the Post Graduate Certificate Programme in Financial Management – IIM Tiruchirappalli. This course will help you understand different aspects, such as financial statements and analysis, valuation, strategic cost management and more.
FAQs
1. What software is commonly used for financial modelling?
Cube, OracleBI and Jirav are some of the most common and widely used software in financial modelling.
2. How can I improve my financial modelling skills?
You can increase your skills and knowledge by doing different courses from authentic platforms, such as Jaro Education. Notably, a certified course can help you develop more skills. Besides, some of the techniques that you should follow to improve your financial modelling skills are:
- Planning and outlining
- Maintaining quality
- Regular accuracy checks
3. What are the career opportunities for financial modellers?
Investment bankers, equity research analysts, CFOs, private equity professionals, management consultants and accountants are some career paths for financial modellers.
4. How do financial models help in risk management?
Financial models analyse several factors of return on investment, business growth, rate of inflation, interest rates, and other variables comprehensively, giving board members a fair idea about future risks and how to manage them.
5. Are there any regulatory requirements for financial modelling in certain industries?
There are no regulatory requirements for financial modelling.







